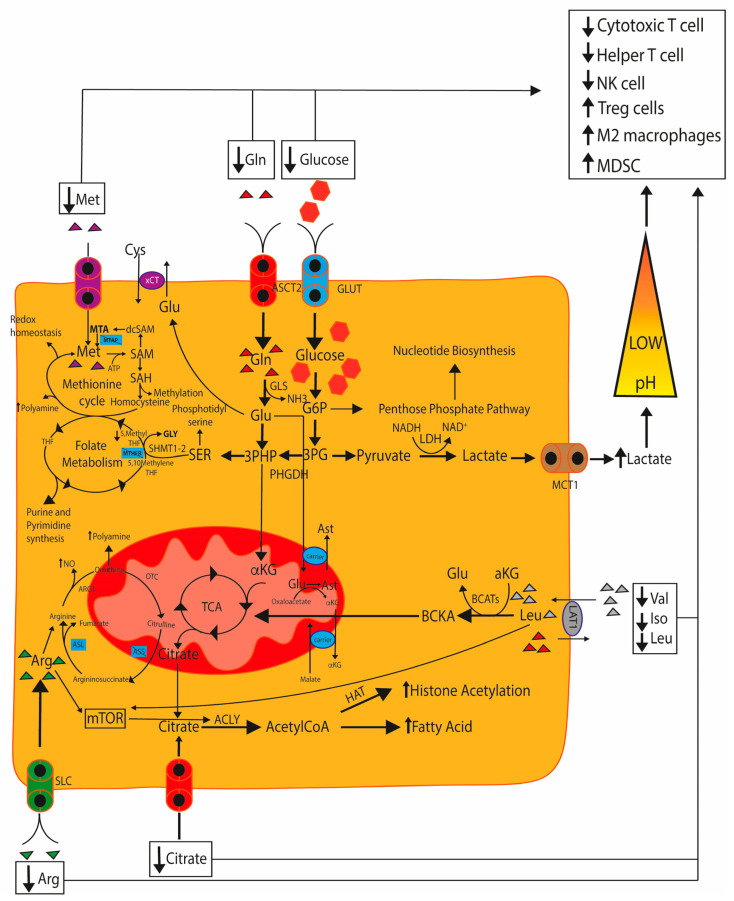
Figure 4.
Cancer metabolism promotes immunosuppressive TME. Cancer cells mainly rely on glycolysis as it supports the biosynthesis of nucleotide, via penthose phosphate pathway and folate metabolism cycle, and molecules involved in controlling the redox state of the cell, via methionine cycle. LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; 3PG: 3-phosphoglyceric acid; 3PHP: 3-phospho-hydroxypyruvate; Glu: glutamate; α-KG: α-ketoglutarate; TCA: tricarboxylic acid cycle; ACLY: ATP citrate lyase; OXPHOS: oxidative phosphorylation; MAS: malate-aspartate shuttle; xCT: Cystine/Glutamate Antiporter; MTAP: methylthioadenosine phosphorylase; MTHFR: methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase; ASS1: arginine synthase 1; ASL: argininosuccinate lyase; Arg: arginine; SLC6A14, SLC7A3, SLC7A9: arginine transporters; NO: nitric oxide; ARG1: arginase 1; Lat1: branched amino acids transporter; BCKA: branched-chain α-ketoacids.