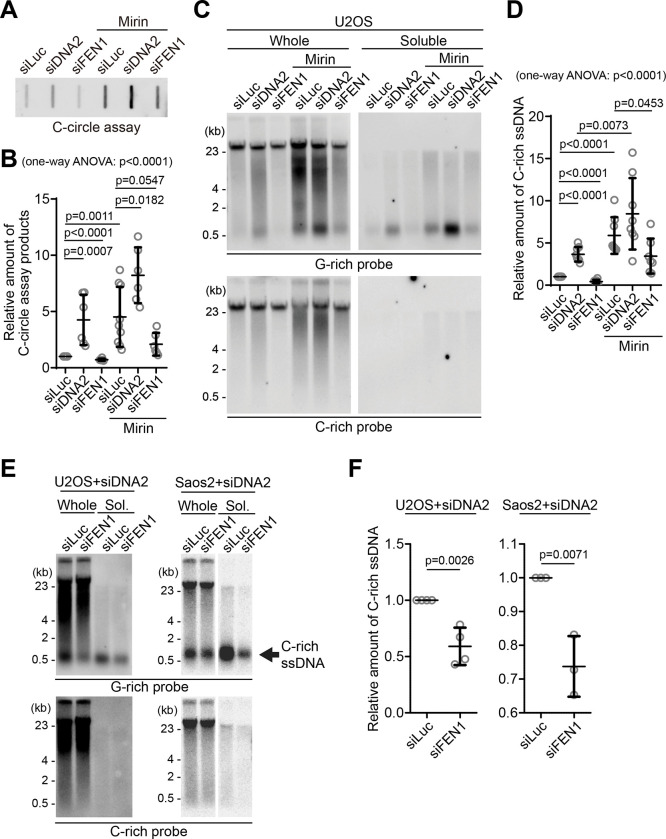
Figure 4. C-circles and C-rich ssDNAs are generated during Okazaki fragment processing.
(A) C-circle assay for U2OS cells after transfection of siRNAs targeting DNA2 or FEN1 with or without Mirin treatment. DNA amount: 40 ng. (B) Quantification of the C-circle assay in A as the relative amount of C-circle assay products (mean ± SD; unpaired t-test). One-way ANOVA analysis; p<0.0001. (C) 4SET assay for U2OS cells after transfection of siRNAs targeting FEN1, DNA2, or control (siLuc) with or without Mirin treatment. Samples were fractionated into whole DNA or soluble fraction. DNA amount (whole: 210 ng, soluble: 70 ng). G-rich probe was used to detect C-rich telomeric sequences, and C-rich probe was used to detect G-rich telomeric sequences. (D) Quantification of the C-circle assay in C; as the relative amount of C-rich ssDNA (whole). (mean ± SD; unpaired t-test). One-way ANOVA analysis; p<0.0001. (E) 4SET assay for U2OS and SaoS2 cells after transfection of siRNAs targeting FEN1 and DNA2, or DNA2 and siLuc. DNA amount (whole: 210 ng, soluble: 70 ng). G-rich probe was used to detect C-rich telomeric sequences, and C-rich probe was used to detect G-rich telomeric sequences. C-rich single stranded DNAs are indicated by an arrow. (F) Quantification of the 4SET assay in E; as the relative amount of C-rich ssDNA (whole). (mean ± SD; unpaired t-test).