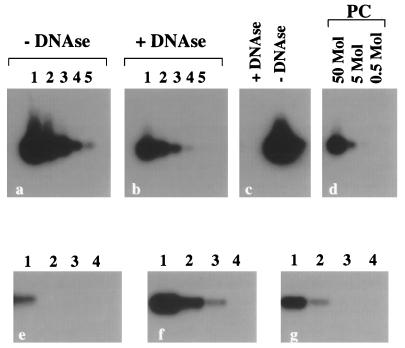
FIG. 3.
Inhibition of the production and/or release of free virus in supernatants from TPA-induced BCBL-1 cells by IFN-α2b. The cells were induced for 5 days and analyzed for cell viability and numbers by trypan blue exclusion. The proportions of viable (blue trypan-excluding) cells were 83% in the control (uninduced) culture, 72% in the TPA-induced culture, and 86% in the culture induced with TPA in the presence of αIFN. (a and b) Supernatants from TPA-induced BCBL-1 cells before (a) or after (b) DNase treatment. (c) DNase treatment of culture medium containing 100 ng of plasmid p1.8Kb encompassing the HHV-8 PCR target sequences. (d) Positive-control PCR performed with the indicated amounts of plasmid p1.8Kb. (e to g) DNase-treated supernatants from BCBL-1 cells uninduced (e) or induced (f and g) with TPA in the absence (e and f) or presence (g) of IFN-α2b (25 IU/ml). Lanes: 1, starting dilution corresponding to supernatants derived from 15 cells; 2 to 5, serial dilutions (1:5). DNase I digestion resulted in a fivefold decrease of HHV-8 DNA in both TPA-induced and -uninduced cell cultures (data not shown). Cells cultured for 24 h in the presence or absence of IFN-α2b (25 IU/ml) were induced with TPA (20 ng/ml) for 5 days, and supernatants were analyzed by semiquantitative PCR. Shown is the autoradiogram of the HHV-8 PCR products (primers KS1 and KS2) hybridized with a specific oligonucleotide probe.