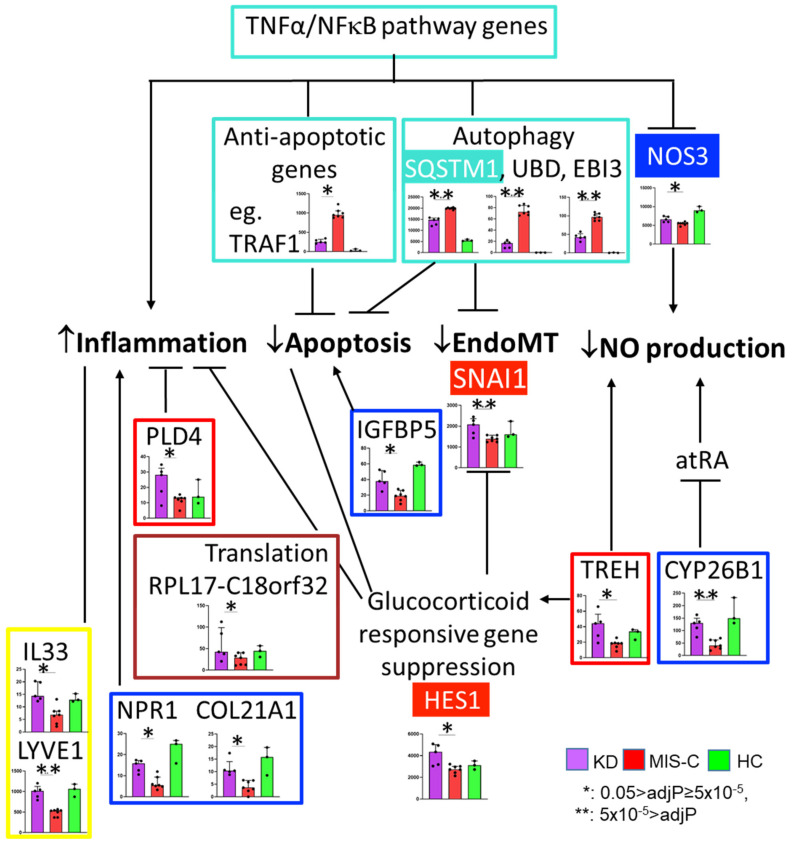
Figure 5.
Suggested biological meaning at the intersection of the gene modules from network analysis and 41 DEGs between MIS-C and KD. Color-coded boxes represent the gene modules from WGCNA. Genes in filled boxes were not among the 41 DEGs but were key molecules in the WGCNA modules. SQSMT1, UBD, and EBI3 have important roles in protein degradation [32,33], and SQSTM1-dependent degradation of snail (SNAI1), a transcription factor regulating EndoMT, has been reported [34]. Cytochrome P450 family 26 subfamily B member 1 (CYP26B1) and trehalase (TREH) are genes that influence NO production in ECs [35,36]. TREH also induces functional confirmation in the glucocorticoid receptor [37]. IGFBP5 relates to apoptosis [38]. Relation with inflammation was reported for PLD4 [39], NPR1 [40], COL21A1 [41], IL33 [42], and LYVE1 [25]. The effects of IL-33 are either pro- or anti-inflammatory, depending on the disease. LYVE1 is important for leukocyte trafficking. Post-transcriptional regulation of CCL2 by GC is well reported [43]. GC binds to GC receptor (GR) in the cytosol and exerts its anti-inflammatory functions by inhibiting expression of cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules in ECs [44]. GC has tissue-specific action on apoptosis [45]. GC inhibits protein synthesis by inhibiting translation initiation and ribosomal synthesis at the levels of transcription, post-transcription, and translation [46,47,48]. RPL17-C18orf32 is a read-through transcript between RPL17 (ribosomal protein L17) and C18orf32 (chromosome 18 open reading frame 32) genes.