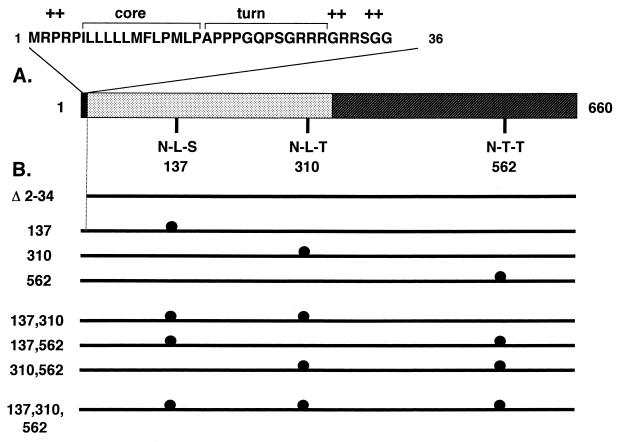
FIG. 1.
ORF2 features and mutants. (A) The 660-amino-acid protein (pORF2) encoded by HEV ORF2 is shown schematically, with two major regions: the extreme N terminus, containing the putative signal sequence (filled), and the basic highly N-terminal half of the protein, containing about 10% arginine residues (dotted). The extreme N-terminal region is expanded to show three domains characteristic of eukaryotic signal sequences, the hydrophobic core domain, a region containing turn-inducing amino acids, and a positively charged domain (+). The positions of three potential N-linked glycosylation sites (N-X-S/T) are shown at amino acid residues 137, 310, and 562 in the primary sequence of pORF2. (B) Various mutants used in this study are shown schematically. The Δ2-34 mutant carries a 5′-end deletion in ORF2 corresponding to amino acids 2 to 34 in the polypeptide sequence. The glycosylation mutants with Asn→Ala changes at the indicated positions are shown (●). The nomenclature corresponds to the amino acid position(s) changed in that particular mutant.