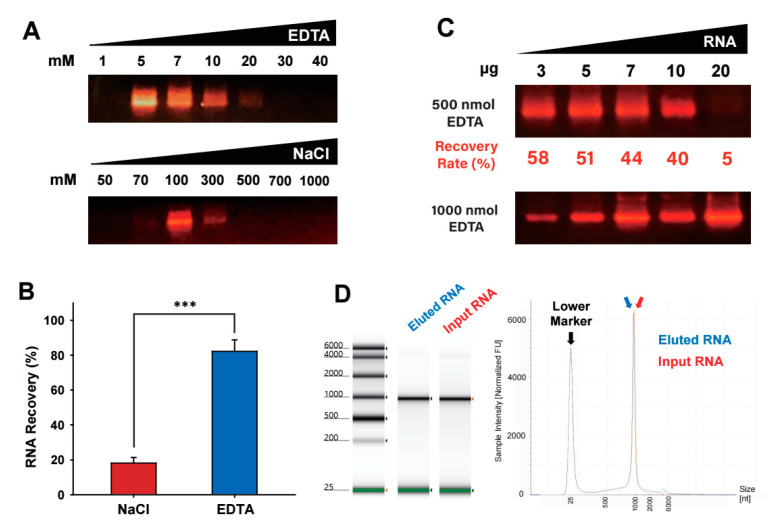
Figure 4.
Evaluation of the elution reagents for recovery of silica-adsorbed RNA. The LiCl-precipitated IVT RNA (10 μg) was purified by spin column-based mesoporous silica chromatography using elution buffer containing either EDTA or NaCl with stepwise gradient concentrations. (A) Comparison of RNA recovery with salt (NaCl) and chelating reagent (EDTA) as an eluting reagent at a stepwise increase of concentration. Each eluant fraction was electrophoresed in 1.0% agarose gel pre-stained with GelRed, and RNA was visualized under UV illumination. (B) RNA recovery rate in each elution reagent was combined and normalized to the initial amount of input RNA. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation, n = 3; *** p < 0.005, NaCl vs. EDTA. (C) Various amounts of RNA were mixed with spermidine at a fixed N/P ratio of 20 and purified by spin column-based mesoporous silica chromatography by elution with 500 nmol and 1000 nmol EDTA. Each eluant fraction was electrophoresed in 1.0% agarose gel prestained with GelRed, and the RNA present in each fraction was visualized with UV transillumination. The recovery rates of eluants with 500 nmol EDTA were calculated by quantifying the amount of RNA using the RiboGreen assay. (D) Assessment of RNA quality in size, recovery rate, and intactness. The recovered RNA from the mesoporous silica-based chromatography through EDTA elution, as performed in (A), was analyzed by a capillary electrophoresis system, TapeStation. Gel-like electropherogram and elution profile were displayed for comparison of the input RNA and the EDTA-eluted RNA.