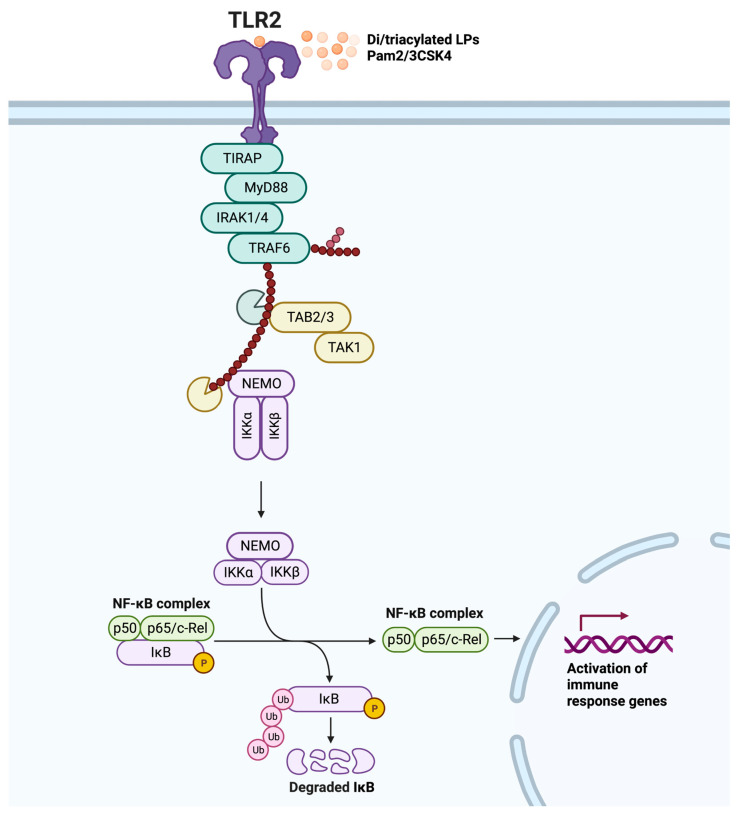
Figure 1.
TLR2 MyD88-dependent signaling pathway. Dimerization is triggered by ligand binding (diacylated lipopeptides (LPs) or triacylated LPs, and synthetic Pam2CSK4 or Pam3CSK4), resulting in a signaling cascade that begins with Toll-interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing adaptor protein (TIRAP) binding to TLR2, which then leads to the recruitment of MyD88. Following phosphorylation of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) 4, IRAK1, and IRAK2, TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) undergoes K63-linked autoubiquitination and ubiquitinates nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) essential modulator (NEMO). The complex of transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase-1 (TAK1), TAK1-binding protein 2 (TAB2), and TAB3 complex is then activated to phosphorylate IkappaB kinase alpha (IKKα) and IKKβ, and the IKKs phosphorylate IκB, marking it for degradation and releasing the NF-κB complex (consisting of p50 and p65/c-Rel). This ultimately leads to the activation of immune response genes, including the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines via the transcription factor NF-κB. Adapted from “NF-KB signaling pathway”, by BioRender.com (2023).