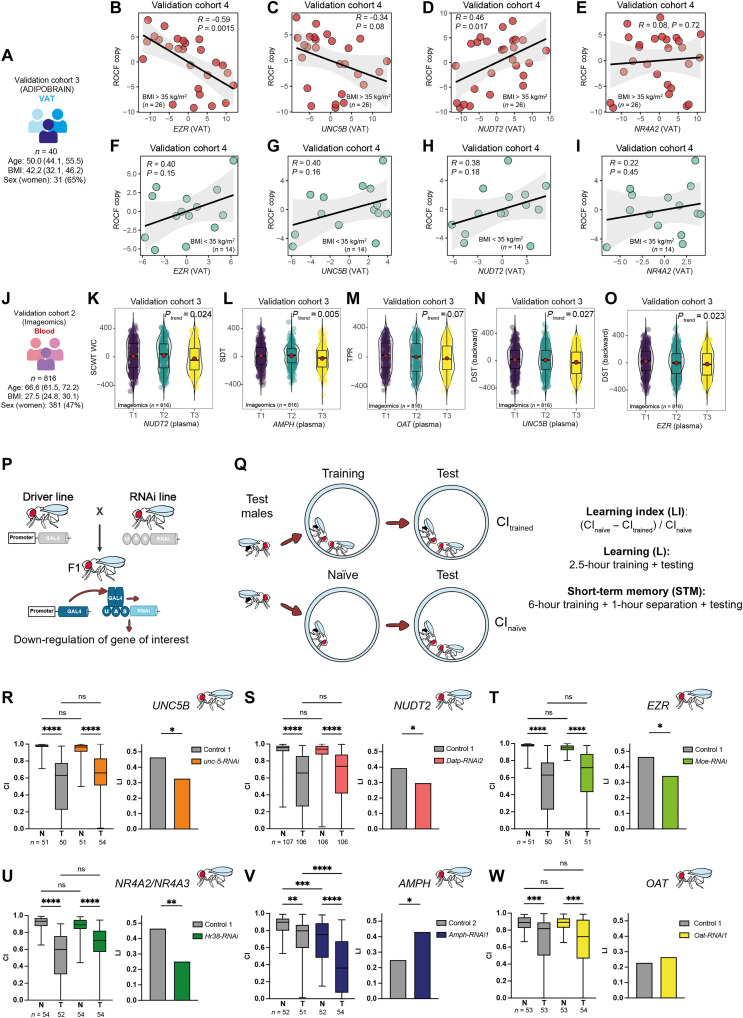
Fig. 5. Associations of expression levels of selected genes with cognition in a validation cohort, the Aging Imageomics cohort, and D. melanogaster.
(A) Main baseline characteristics of the validation cohort 3 (ADIPOBRAIN). Scatter plots of the partial Spearman’s rank correlations (adjusted for age, BMI, sex, and education years) between ROCF copy scores and the VAT expression levels of (B) EZR, (C) UNC5B, (D) NUDT2, and (E) NR4A2 in patients with a BMI of >35 kg/m2 from the ADIPOBRAIN cohort. (F to I) The same associations but in patients with a BMI of <35 kg/m2. (J) Main baseline characteristics of the validation cohort 2 (Imageomics). Violin plots of the score in several cognitive tests and the tertiles (T1, T2, and T3) of the circulating expression levels of selected genes: (K) normalized STROOP color word test–color word (SCWT CW) versus NUDT2; (L) symbol digit test (SDT) versus AMPH; (M) total paired recall (TFP) versus OAT; (N) normalized digit span test (DST) backward versus UNC5B; and (O) normalized DST backward versus EZR. The ranked residuals after controlling for age, BMI, gender, and education level are plotted. Overall significance was assessed using a Mann-Kendall trend test. (P) Scheme of the RNA interference via the UAS-GAL4 system. (Q) Courtship conditioning paradigm. (R to W) The graphs display courtship conditioning paradigm results of fat body promoter line w; C7-GAL4; UAS-Dcr-2 crossed with RNAi lines targeting (R) unc-5, (S) Datp, (T) Moe, (U) Hr38, (V) Amph, (W) Oat, and their corresponding genetic background controls (controls 1 and 2). Boxplots represent the CI of naïve (N) and trained (T) males. Significance of courtship suppression upon training was assessed with Kruskal-Wallis nonparametrical test and post hoc Dunn’s multiple comparison test. LI statistical significance was determined with the nonparametrical bootstrap analysis with 10,000 iterations. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001. ns, not significant.