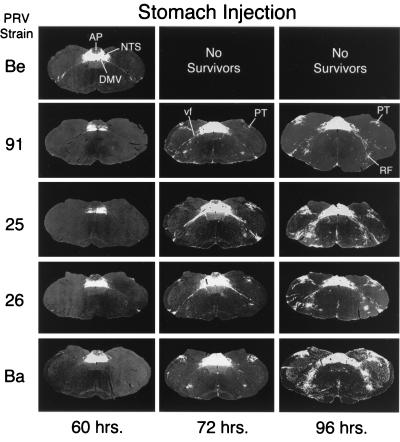
FIG. 2.
Low-power photomicrographs illustrate the progression of infection in the caudal brainstem 60, 72, and 96 h following injection of strains of PRV. Negative images, where viral immunoreactivity is revealed as a white signal on a dark background, are shown. PRV-Becker (PRV-Be), a wild-type strain of PRV, infects a large number of neurons in the DVC (DMV, NTS, and AP) 60 h postinoculation, but only scattered neurons are infected in the ventrolateral portion of the medulla. Animals infected by this virus did not survive beyond 67 h in this study. Photomicrographs in other rows illustrate the patterns of infection produced by PRV-91, PRV-25, PRV-26, and PRV-Bartha (PRV-Ba). PRV-Ba, an attenuated vaccine strain harboring a number of deletions and mutations, produces the most-extensive infection at all postinoculation intervals. PRV-25, PRV-26, and PRV-91 infect a subset of the circuitry infected by PRV-Ba, but they still produce extensive retrograde infections. RF, reticular formation.