Figure 2. Secondary screening of candidate and variant rFVIII-targeting photo-responsive CAP ligands.
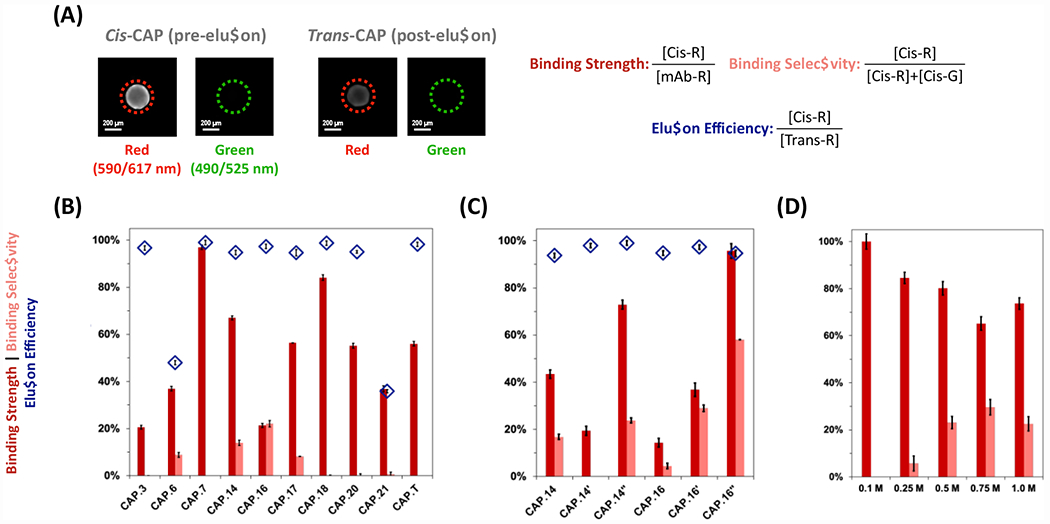
(A) The values of rFVIII binding strength were calculated as the ratio between the corrected intensity of red fluorescence (exc/em: 590/617 nm) of a cis-CAP-ChemMatrix bead and the corrected intensity of a control ChemMatrix bead (i.e. functionalized with anti-rFVIII antibodies) following AF594-rFVIII adsorption. The values of rFVIII binding selectivity were calculated as the ratio of the corrected intensity of red fluorescence of a cis-CAP-ChemMatrix bead after AF594-rFVIII adsorption against the total red and green (exc/em: 490/525 nm) fluorescence of a cis-CAP-ChemMatrix bead after AF594-rFVIII and AF488-HCPs adsorption. The values of rFVIII elution efficiency were calculated as the ratios of the corrected red fluorescence intensity of a cis-CAP-ChemMatrix bead after AF594-rFVIII adsorption and the corrected red fluorescence intensity of the same trans-CAP-ChemMatrix bead after AF594-rFVIII desorption upon exposure to visible light (λex = 420-450 nm) at ~220 mW·cm−2 for 2 mins at room temperature (25°C). Scale bar = 200 μm. (B) Sequences selected for in vitro analysis of rFVIII binding strength (dark red), elution efficiency (light red), and selectivity (blue diamonds), (C) their structural variants, and (C) performance of at different values of ionic strength of the mobile phase – namely, X M NaCl (X: 0.1, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, and 1) added to 0.1 M HEPES buffer, 5 mM CaCl2, and 0.01% v/v Tween20 at pH 7.4. Error bars represent one standard deviation of 30 beads. The raw values of average fluorescence and are in Figure S4.
