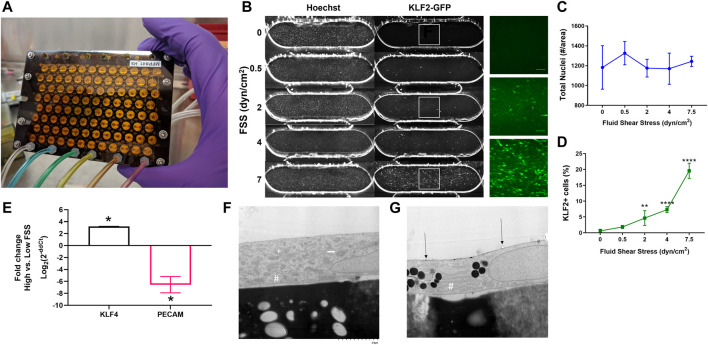
FIGURE 3.
Validation of high flow pump and EC response to FSS. (A) Photo of the pneumatically actuated PREDICT96 high flow pump lid showing 96 arrayed micro-pumps. (B) Representative images of Hoechst stain and KLF2-GFP expression in reporter EC subjected to different FSS conditions. Insets show close-up of KLF2 for select conditions. Quantification of (C) total nuclei and (D) KLF2 expression as a function of FSS. **p < 0.005, ****p < 0.0001 for one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test for n = 4-8 devices per condition. (E) Comparative gene expression for shear-responsive genes in retinal microvascular ECs; positive values indicate upregulation with exposure to high FSS (7 dyn/cm2) relative to low FSS (0.5 dyn/cm2), while negative fold change indicates downregulation. (F) Electron micrograph showing ultrastructure of retinal microvascular EC under low FSS, exemplified with cytoplasmic organelles, including rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER; #), Golgi (+), and mitochondria (white arrow). (G) Electron micrograph of EC under physiological FSS with more abundant RER and electron dense bodies consistent with lipids are observed. Gold particle labeling indicated by black arrows. Images at x7000 magnification.