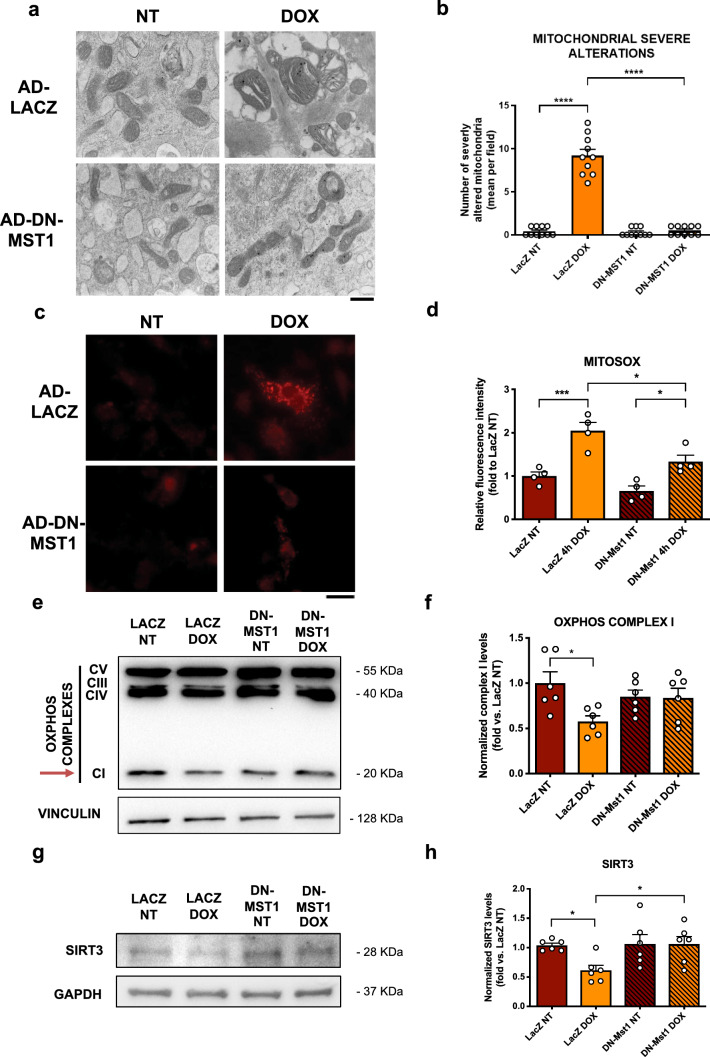
Fig. 2.
MST1 inhibition attenuates DOX-induced mitochondrial oxidative stress and preserves SIRT3 expression levels, a Representative TEM images of myocardial mitochondria from cardiomyocyte cultures infected with ad-LacZ or ad-DN-MST1 for 48 h and then treated with doxorubicin (50 μM) for four hours. Scale bar = 0.4 μm; b quantification of the number of mitochondria presenting severe alterations per microscopic field. Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 10 microscopic fields from 5 independent samples); c–d MitoSOX staining of cardiomyocyte cultures infected with ad-LacZ or ad-DN-MST1 for 48 h, and then treated with doxorubicin (50 μM) for four hours. Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 4 independent samples). Scale bar = 25 μm; (e–f) OXPHOS complexes expression profile and complex I quantification from cardiomyocyte cultures infected with ad-LacZ or ad-DN-MST1 for 48 h, then treated with doxorubicin (50 μM) for four hours. Densitometric data normalized by loading control represent mean ± SEM (n = 6 independent samples); g–h SIRT3 expression profile in cardiomyocytes infected with ad-LacZ or ad-DN-MST1 for 48 h, and then treated with doxorubicin (50 μM) for four hours. Densitometric data normalized by loading control represent mean ± SEM (n = 6 independent samples). Data were analysed with one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc test. *P ≤ 0.05; ***P ≤ 0.001; ****P ≤ 0.0001