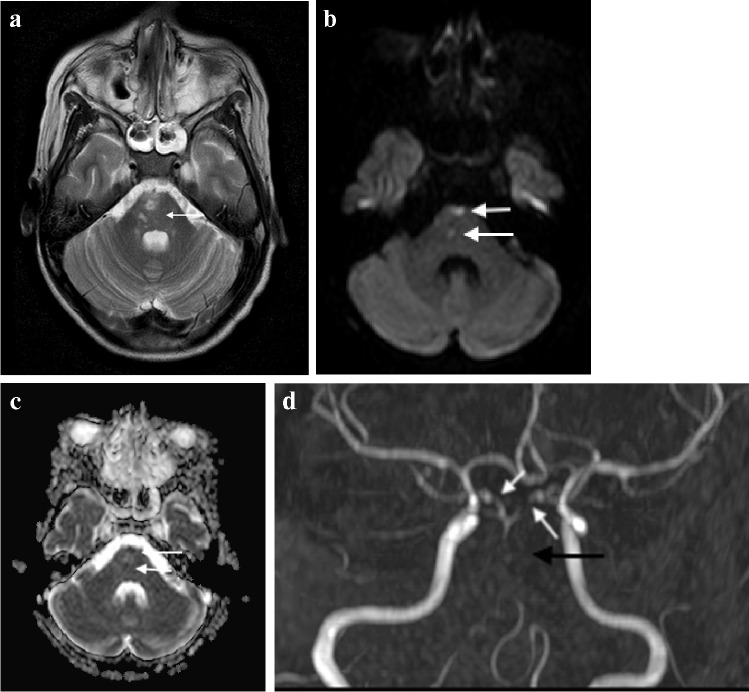
Fig. 19.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in a 12-year-old boy with tuberculous meningitis and persistent decreased level of consciousness. a Axial T2 demonstrates multiple hyperintense foci in the pons (arrow). b Axial diffusion-weighted image demonstrates restricted diffusion (arrow) c Low signal (arrows) on the apparent diffusion coefficient map confirms infarcts. d Coronal magnetic resonance angiogram image shows partial occlusion of the basilar artery (black arrow) and irregularity of both posterior communicating arteries (white arrows)