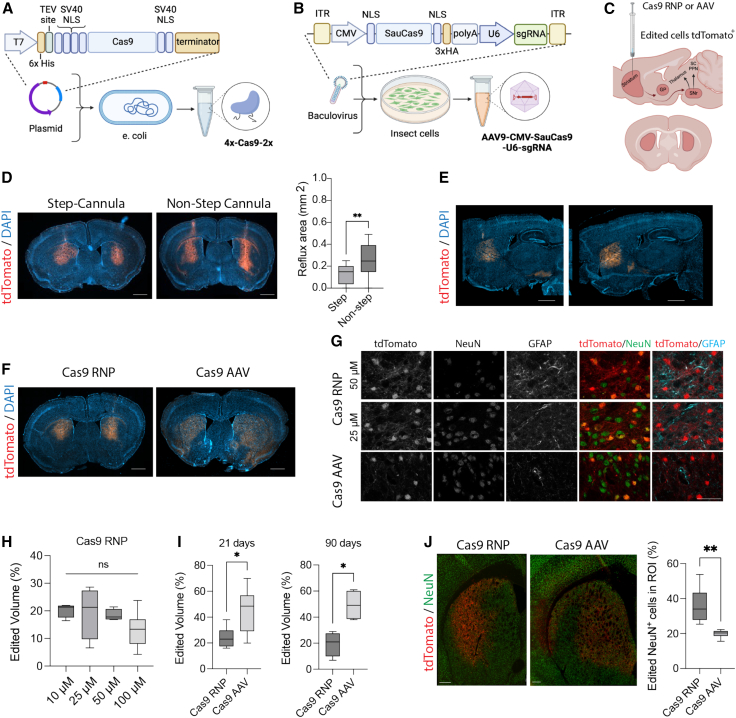
Figure 1.
In vivo editing at tdTomato locus with viral and non-viral Cas9 delivery strategies
(A) Schematic of 4x-SpyCas9-2x cell-penetrant protein expression and purification systems, (B) AAV9-SauCas9-sgRNA expression and purification systems, and (C) expected edited brain regions in the basal ganglia shown in sagittal view (top) and coronal view (bottom). Striatal neurons extend into the globus pallidus and substantia nigra. Created with BioRender.com. (D) Comparison of convection-enhanced delivery (CED) of cell-penetrant 4x-SpyCas9-2x RNP with step and non-step cannulas (n = 3–6 injections per group, unpaired t test, ∗∗p < 0.01.) Scale bars, 1 mm. (E) Serial sections of single hemisphere sagittal view of edited tdTomato+ cells in the basal ganglia circuit after injection of Cas9 RNP with CED into the striatum. Scale bar, 1 mm. (F) Representative coronal section of the striatum of mice that received Cas9 RNPs and AAVs at 21 days post-injection, showing the distribution of tdTomato+ edited cells. Scale bar, 1 mm. (G) Co-staining of tdTomato with NeuN and GFAP in the striatum at 90 days post-injection. Scale bar, 50 m. (H) Volume of edited striatal tissue as the concentration of injected Cas9 RNPs was increased from 10 to 100 M (n = 4–6 injections, one-way ANOVA, ns). (I) Quantification of editing following treatment with Cas9 AAV (3e-9 vg/L, 1.5e-10 vg/hemisphere) and Cas9 RNPs (25 M, 125 pmol/hemisphere) at 21 and 90 days (n = 4–6 injections, one-way ANOVA, ∗p < 0.05). (J) Co-expression of tdTomato and NeuN quantified per regions of interest (ROIs), e.g., edited area per hemisphere (n = 4–6 injections, one-way ANOVA, ∗∗p < 0.01). Scale bars, 250 m.