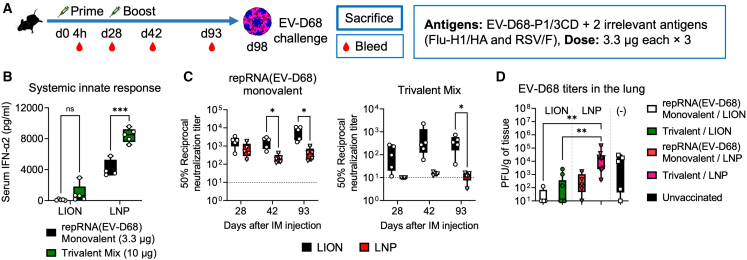
Figure 5.
Intramuscular injection of multivalent repRNA/LION but not repRNA/LNP induces a neutralizing antibody response in mice
(A) The experimental design for analyzing the adaptive immune response to the multivalent antigens encoded in repRNA in mice. C57BL/6 mice received i.m. injection of repRNA encoding three indicated antigens (EV-D68 P1/3CD, Flu/H1-HA, and RSV/F) (3.3 μg each) formulated with LION or LNP at days 0 and 28. (B) Serum IFN-α2 levels at 4 h after the prime dose were determined by ELISA and shown as boxplots. Min to max values with all data points are shown (n = 4–5). (C) EV-D68 neutralizing activity of sera of vaccinated mice was measured by neutralization assay. Geometric means with each individual value are shown as bars and symbols (n = 4–5). (B and C) Statistical comparison of mean values among groups was performed by multiple unpaired t tests between values in the monovalent group vs. values in the trivalent mix group (B) for each formulation, or values in the LION group vs. values in the LNP group at each time point (C). (D) EV-D68 titers in the lung of infected mice were determined by plaque assays (n = 5–10). Min to max values with all data points are shown. Statistical comparison of mean values among groups was performed by Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn’s multiple comparisons test between the values in each group. Unless otherwise noted, only statistically significant results are shown as asterisks: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; ns, not significant.