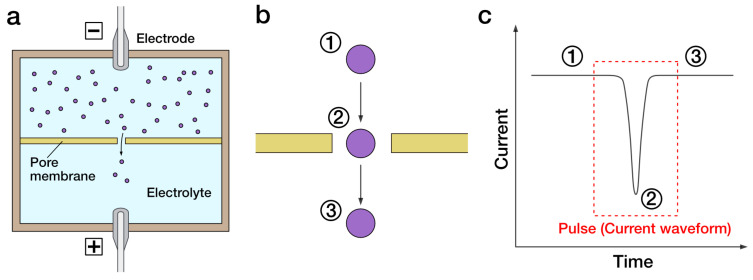
Figure 9.
Schematic illustration of pore-based sensing. An electrolyte is divided by a pore membrane, and electrodes are placed on each (a). When voltage is applied to the electrodes, an ion current is generated that passes through the pore membrane, and the small particles (indicated as purple circles) in the solution pass through the pores by electrophoresis or electroosmotic force. Particles passing through the pore (One particle moves to ➀, ➁, ➂ in order) block the ion current (b), and the corresponding current value change is measured as a pulse (c).