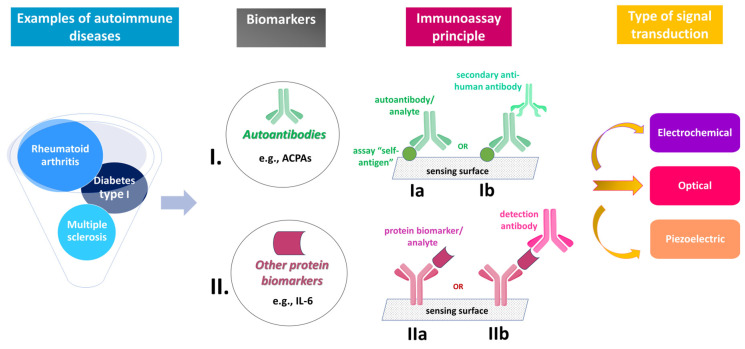
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the main principles on which immunosensors for autoimmune diseases (AD immunosensors) developed to date are based. The sensors can be divided into two broad categories, i.e., those detecting autoantibodies (I) and those detecting other protein biomarkers (II). All sensors are based on a non-competitive immunoassay principle. The sensors of group I follow a direct-type immunoassay setting (Ia), in which an anti-human secondary antibody may also be used (Ib). The sensors of group II may follow either a direct-type (IIa) or a sandwich-type (IIb) immunoassay setting; in the latter, a couple of capture and detection anti-analyte antibodies (often along with a secondary antibody, for signal enhancement) are employed. Depending on their signal transduction principle, the AD immunosensors may be classified as electrochemical, optical, or piezoelectric.