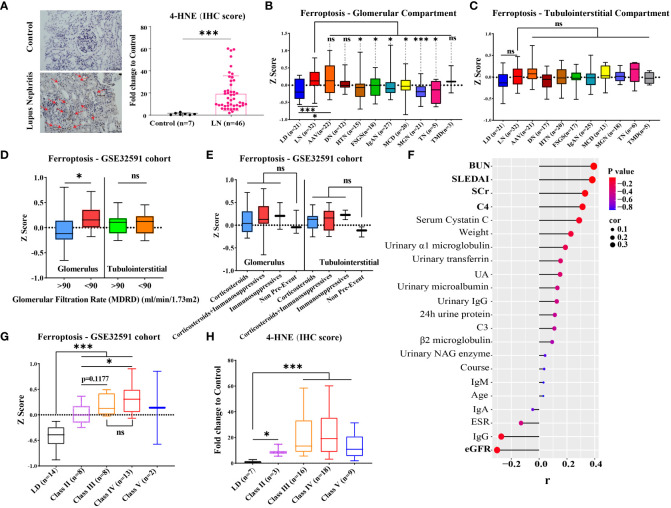
Figure 2.
Level of ferroptosis in LN and other kidney diseases and association with kidney function. (A) Representative immunohistochemistry images of 4-HNE in 46 LN patients and seven LDs. The red arrows indicate 4-HNE-positive regions. (B, C) Gene expression of ferroptosis within the glomerular and tubulointerstitial compartments of various renal diseases and living donors in GSE104948/54 cohort. (D) Gene expression of ferroptosis within the glomerular and tubulointerstitial compartments in distinguishing LN patients (GSE32591 cohort) with GFR ≥ 90 from those with GFR < 90. (E) Gene expression of ferroptosis within the glomerular and tubulointerstitial compartments in LN patients (GSE32591 cohort) with treatment by concomitant glucocorticoid and/or immunosuppressants. (F) Correlation of 4-HNE level and clinical features of 46 LN patients in our own LN cohort. (G, H) Gene expression of ferroptosis within the glomerular compartments in different classes of LN patients from GSE32591 cohort (G) and our own LN cohort (H). LD, living donors; LN, lupus nephritis; AAV, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis; DN, diabetic nephropathy; HTN, hypertensive nephropathy; IgAN, IgA nephropathy; FSGS, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis; TMD, thin membrane disease; MCD, minimal change disease; MGN, membranous glomerulonephropathy; TN, tumor nephrectomy; IHC, immunohistochemical; SLEDAI, systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; C3/C4, complement 3/4; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; SCr, serum creatinine; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; UA, uric acid. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001; ns, not significant. Values of p < 0.05 were considered significant.