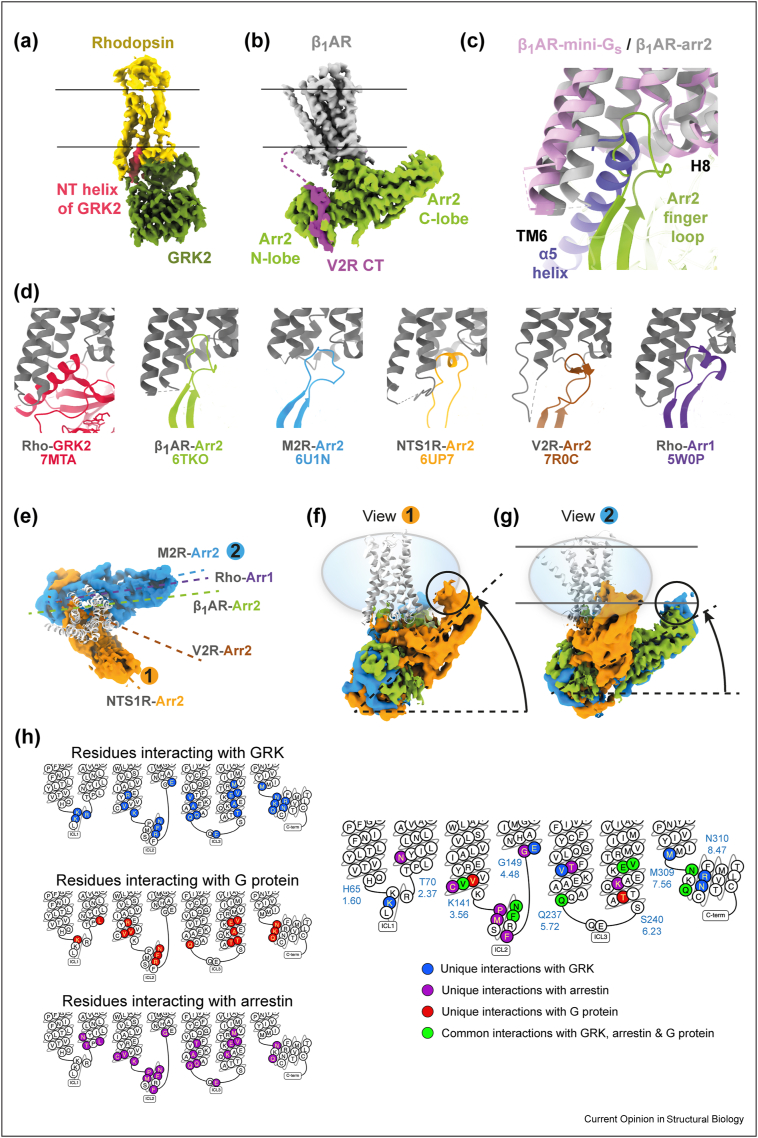
Figure 2.
Variations in coupling of arrestins and GRK2 to GPCRs. (a) Cryo-EM density (EMDB-23979) of rhodopsin coupled to GRK1 [33]. Density for the Fab required for structure determination has been removed for clarity. (b) Cryo-EM density of β1AR in a lipid nanodisc coupled to β-arrestin1 (EMDB-10515) [37]. Density for Fab30 required for structure determination has been removed for clarity. (c) Superposition of β1AR coupled to mini-Gs (purple; PDB code 7JJO [72]) and β1AR (grey) coupled to β-arrestin1 (green; PDB code 6TKO [37]). (d) Different conformations of the GRK coupling helix and arrestin finger loop when coupled to different receptors. (e–g) Variation in the angle of arrestin coupled to different receptors (see main text for references): (e) a view perpendicular to the membrane plane; panels (f–g) are views parallel to the membrane plane in positions 1 and 2, respectively, as defined in panel (e). (h) Snake plots of bovine rhodopsin with amino acid residues within 3.9 Å (inclusive) of either GRK, G protein or arrestin coloured appropriately. PDB codes for the complexes are as follows: rhodopsin-GRK, 7MTB [33••]; rhodopsin-G protein, 6OYA [73]; rhodopsin-arrestin, 5W0P [74]. The panels were made using GPCRdb [75].