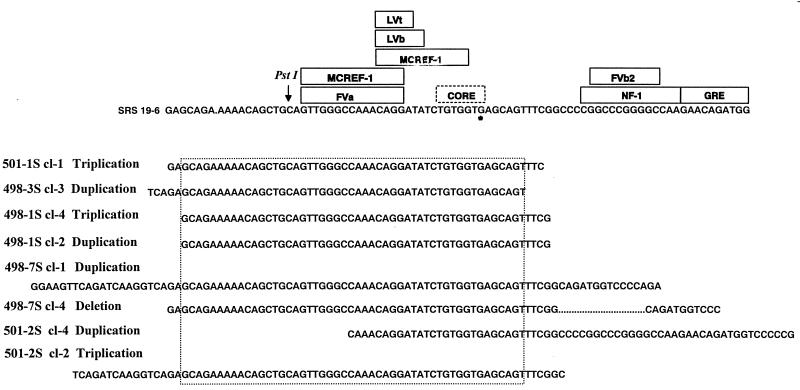
FIG. 6.
Altered SRS enhancer regions amplified from ΔMo+SRS M-MuLV-induced tumors. PCR products of tumors similar to those shown in Fig. 4 were cloned and sequenced. The sequences were aligned with the input SRS enhancer sequences shown at the top of the figure. Binding sites for sequence-specific DNA binding proteins are included (6). The asterisk indicates a G residue that is not present in the standard core motif; it is an A residue in the M-MuLV enhancers. The sequences shown for the different PCR clones indicate sequences that were tandemly duplicated or triplicated. For 498-7S clone 4, the alteration consisted of a deletion (… …) in the NF-1 sequences. Two clones with different sequences were obtained for tumors 498-1S, 498-7S, and 501-2S. Otherwise, the sequences shown represent the predominant PCR products from the respective tumors. Tumors 498-1S, 498-3S, and 498-7S were induced by M-MuLV+ M-MuLV, and tumors 501-1S and 501-2S were induced by ΔMo+SRS+ M-MuLV. A specific region of the SRS enhancers was amplified in at least one of the proviruses in each tumor. The minimum size of the region of common amplification is indicated by the dotted box. This portion of the enhancers contains the highly conserved NF-1, LVb motifs, and core motif that differs from M-MuLV at the nucleotide indicated in the figure.