Abstract

Provided herein are novel pyrazoloquinoline compounds as KRAS inhibitors, their pharmaceutical compositions, the use of such compounds in treating cancer, and processes for preparing such compounds.
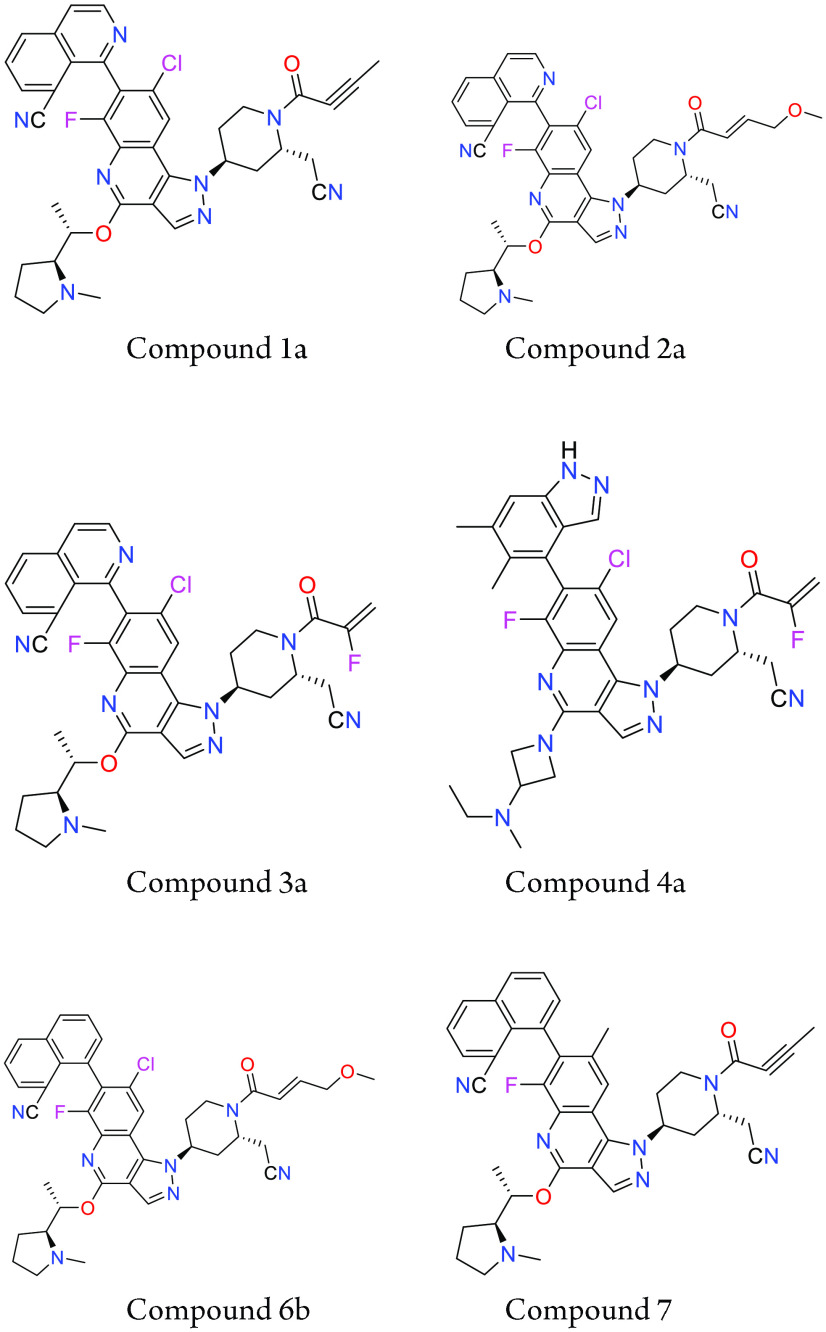
Important Compound Classes

Title
Pyrazoloquinoline KRAS Inhibitors
Patent Publication Number
WO 2023/056421 A1
Publication Date
April 6, 2023
Priority Application
US 63/261,982
Priority Date
October 1, 2021
Inventors
Zhu, W.; Wang, X.; Yao, W.
Assignee Company
Incyte Corporation, USA
Disease Area
Cancer
Biological Target
KRAS
Summary
RAS proteins are part of the family of small GTPases that are activated by growth factors and various extracellular stimuli. The RAS family regulates intracellular signaling pathways responsible for growth, migration, survival, and differentiation of cells. Somatic mutations in RAS may result in uncontrolled cell growth and malignant transformation, while activation of RAS proteins is tightly regulated in normal cells.
The RAS family is comprised of three members: KRAS, NRAS, and HRAS. RAS mutant cancers account for about 25% of human cancers. KRAS is the most frequently mutated isoform, accounting for 85% of all RAS mutations, whereas NRAS and HRAS are found mutated in 12% and 3% of all RAS mutant cancers, respectively. The majority of RAS mutations occur at amino acid residues 12, 13, and 61. KRAS G12D mutations predominate in pancreatic cancers (51%), followed by colorectal adenocarcinomas (45%) and lung cancers (17%), while KRAS G12V mutations are associated with pancreatic cancers (30%), followed by colorectal adenocarcinomas (27%) and lung cancers (23%). In contrast, KRAS G12C mutations predominate in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), comprising 11–16% of lung adenocarcinomas and 2–5% of pancreatic and colorectal adenocarcinomas. The role of mutant KRAS as an oncogenic driver is further supported by extensive in vivo experimental evidence showing mutant KRAS is required for early tumor onset and maintenance in animal models.
The present application describes a series of novel pyrazoloquinoline compounds as KRAS inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. Further, the application discloses compounds, their preparation, use, and pharmaceutical composition, and treatment.
Definitions
Key Structures
Biological Assay
The KRAS G12C exchange assay, KRAS G12C pERK assay, and KRAS G12C WB pERK assay were performed. The compounds described in this application were tested for their ability to inhibit KRAS. The KRAS G12C exchange IC50, KRAS G12C pERK IC50, and KRAS G12C WB pERK IC50 values are shown in the table below.
Biological Data
The following table shows representative
compounds that were tested for KRAS G12C exchange and for KRAS G12C
pERK and KRAS G12C WB pERK inhibition and the biological data obtained
from testing representative examples. For IC50: †
means ≤100 nM.
Claims
Total claims: 31
Compound claims: 20
Pharmaceutical composition claims: 1
Method of treatment claims: 8
Method of inhibition claims: 2
Recent Review Articles
The author declares no competing financial interest.
References
- Sattler M.; Mohanty A.; Kulkarni P.; Salgia R. Precision oncology provides opportunities for targeting KRAS-inhibitor resistance. Trends Cancer 2023, 9, 42–54. 10.1016/j.trecan.2022.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H.; Chi L.; Yu F.; Dai H.; Gao C.; Si X.; Wang Z.; Liu L.; Zheng J.; Shan L.; Liu H.; Zhang Q. Annual review of KRAS inhibitors in 2022. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 249, 115124. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung Y. H.; Choi Y.; Seo H.; Seo M.; Kim H. A conformation-selective protein binder for a KRAS mutant inhibits the interaction between RAS and RAF. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 645, 110–117. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathod L. S.; Dabhade P. S.; Mokale S. N. Recent progress in targeting KRAS mutant cancers with covalent G12C-specific inhibitors. Drug. Discovery Today 2023, 28, 103557. 10.1016/j.drudis.2023.103557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabnis R. W. Novel Tricyclic Compounds as KRAS Inhibitors for Treating Cancer. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2023, 14, 555–556. 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.3c00140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu G.; Chen T.; Zhang X.; Ma X.; Shi H. Small molecule inhibitors targeting the cancers. MedComm 2022, 3, e181. 10.1002/mco2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]