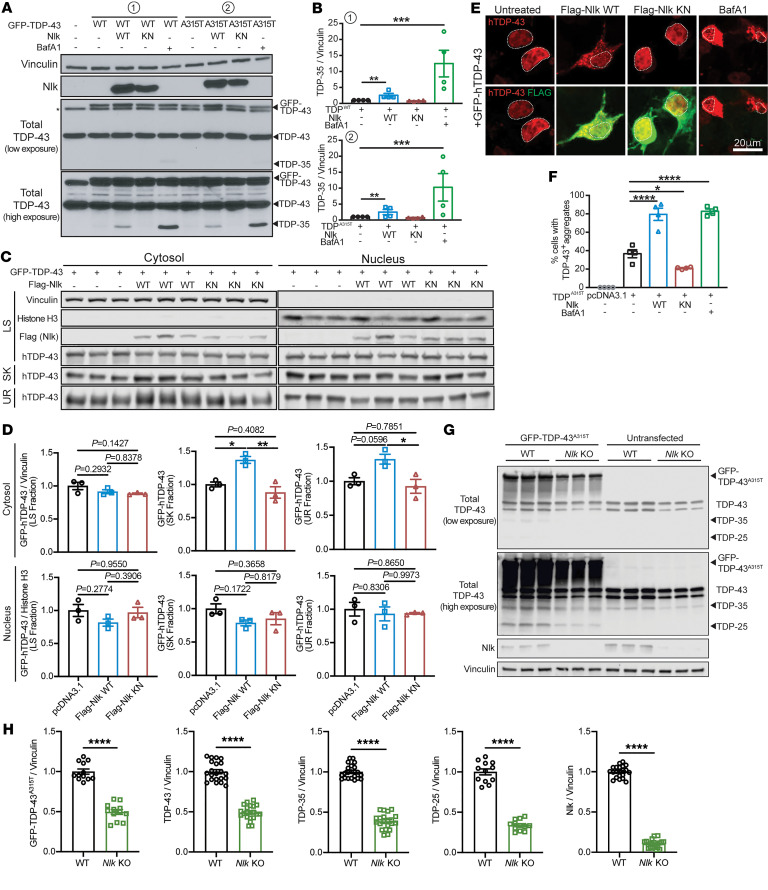
Figure 3. Genetic reduction of Nlk reduces TDP levels in vitro.
(A and B) Western blots showing coexpression of Nlk-WT with GFP-tagged TDPWT or TDPA315T in NSC-34 cells (A) increased levels of TDP-35, while Nlk-KN did not. V-ATPase inhibitor BafA1 treatment similarly increased TDP-35 levels in the absence of Nlk overexpression to an even greater extent. Quantification shows TDP-35 levels in B (n = 4 biological replicates). (C and D) Western blots of sequentially extracted proteins based on detergent solubility from subcellular fractionated NSC-34 cells (C). Quantification of TDP-43 species shows Nlk WT overexpression increased cytosolic insoluble TDP-43 (sarkosyl and urea fractions) (D) (n = 3 biological replicates). LS, low salt; SK, sarkosyl; UR, urea. (E and F) Representative immunostaining of NSC-34 cells cotransfected with GFP-tagged TDP-43 and Nlk showing that WT Nlk increased formation of GFP-positive cytosolic TDP-43 aggregates (E), quantified in F. Nuclei are outlined with dotted lines (n = 4 biological replicates). (G and H) Western blots of cell lysates from WT or Nlk KO N2a cells transfected with GFP–TDP-43A315T (G), quantified in H (n = 12–24 replicates pooled from 4 individual experiments). Levels of exogenous GFP–TDP-43A315T, endogenous TDP-43, and truncated fragments of TDP-43 were significantly reduced. One-way ANOVA analyses (B, D, and F) or 2-tailed t tests (H) were performed to compare all listed genotypes/treatments unless otherwise noted, and data are represented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.