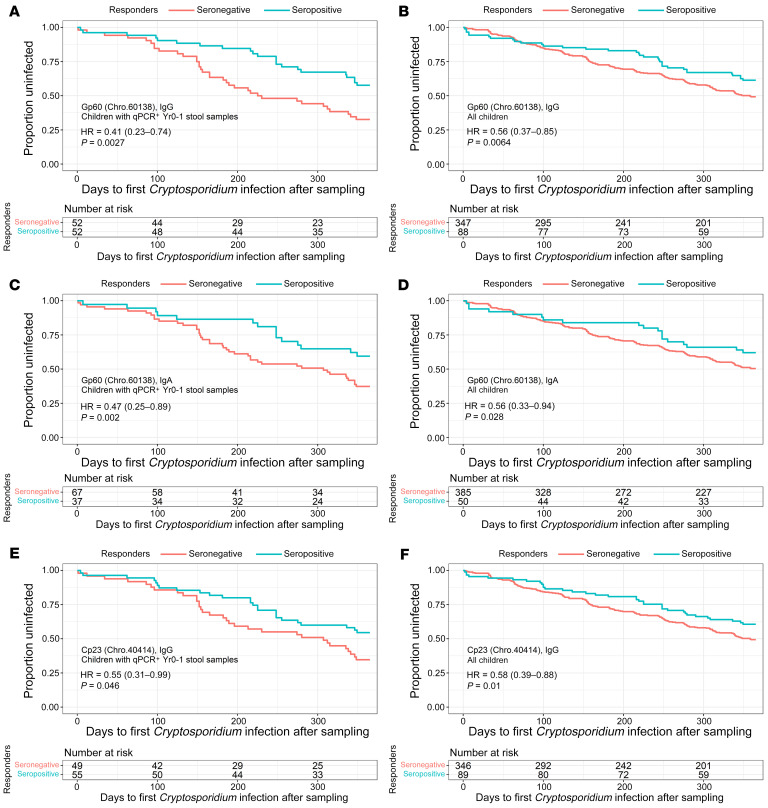
Figure 5. Children with antibodies that targeted the C. hominis peptides encoded by the gp60 gene and Cp23 protein were associated with protection from reinfection.
In the protein array data, IgA and IgG antibodies against the protein encoded by the C. hominis gp60 gene (Chro.60183) and IgG against Cp23 (Chro.40414) were associated with a delay in Cryptosporidium reinfection among children with a qPCR-verified Cryptosporidium infection during the first year of life (A, C, and E) or among all children in the study (B, D, and F). The X-axis shows days after the end of year 1 (when the assayed plasma samples were collected). The Y-axis shows the proportion of children who remained uninfected. Red lines represent children seronegative for the antigen, and blue lines represent seropositive children. The Kaplan-Meier curves show the probability of survival free of Cryptosporidium species, and the tables below the graphs indicate the number of children in the seropositive or seronegative categories at select time points. (A and B) IgG against Gp60 (Chro.60183). (C and D) IgA against Gp60 (Chro.60183). (E and F) IgG against Cp23 (Chro.40414). Hazard ratios (HR), confidence intervals, and P values were calculated using multivariable Cox proportional hazards models.