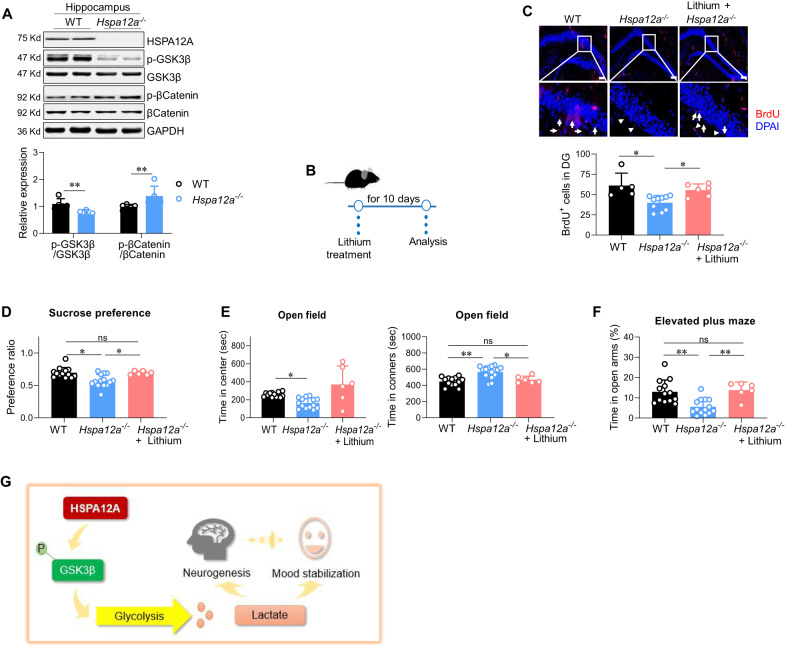
Fig. 5. HSPA12A regulated GSK3β pathway, and GSK-3β inhibitor lithium rescued mood disorder and hippocampal neurogenic impairment in Hspa12a−/− mice.
A Immunoblotting in hippocampus. The indicated gene expression was examined in hippocampus by immunoblotting analysis. n = 5/group. B Experimental protocol. Following lithium treatment for 10 days, the following experiment were performed. C Adult hippocampal neurogenesis (AHN). AHN was examined in granular layer and interspace of dentate gyrus (DG) by BrdU incorporation. DAPI was used to counter stain nuclei. The images showed the representative staining in dentate gyrus, and the boxed areas were magnified in the down panels. n = 5, 10 and 5 for WT, Hspa12a−/−, and lithium-treated Hspa12a−/− group, respectively. Scale bar= 100 μm. D–F Behavioral tests. n = 13 for WT group, n = 14 for Hspa12a−/− group, and n = 6 for lithium-treated group. ns, no significance. G Mechanistic scheme. HSPA12A was required for sustaining cerebral lactate homeostasis to maintain hippocampal neurogenesis and mood stabilization through inhibiting GSK3β in hippocampal neurons. Hippocampal HSPA12A is identified as new regulator of mood behaviors that lends support for its therapeutic potential in mood stabilization. Data are mean ± SD, **P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05 by Mann–Whitney U test (A) and Kruskal–Wallis test (D–F).