Fig. 9. A circuit model for bower behavior and cellular reorganization in Dl, the putative homolog of the hippocampal formation.
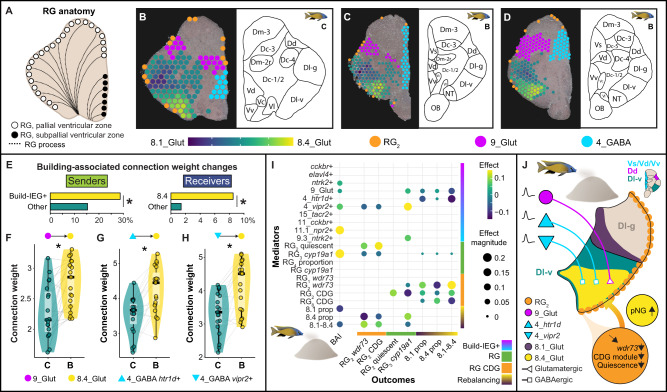
A Radial glia differs in morphology, function, and anatomical distribution (e.g., pallial versus subpallial ventricular zones). B–D RG2 (orange) aligns with the pallial but not subpallial ventricular zone, and 8.1_Glut versus 8.4_Glut aligns with ventral Dl-g versus ventral Dl-v, respectively. E Connections exhibiting building-associated increases in strength were enriched for build-IEG+ senders (yellow, left) and for 8.4_Glut as a receiver (yellow, right; x-axis reflects the percentage of connections exhibiting building-associated changes in weight), asterisks indicate significance at α = 0.05. F–H Building is associated with increased connection weights from senders F 9_Glut, G 4_GABA htr1d+, and H 4_GABA vipr2+ to 8.4_Glut (receiver), n = 38 biologically independent animals (n = 19 building males, n = 19 control males), asterisks indicate effects that were significant at α = 0.05 after adjusting for 5% false discovery rate. In all box plots, the center line indicates the median, the bounds of the box indicate the upper and lower quartiles, and the whiskers indicate the 1.5x interquartile range. Gray lines link paired building/control males. I Regularized multiple mediation analyses identified top candidate regulators of behavior (left column) and supported directional interaction among build-IEG+ populations, radial glial subpopulations, and hippocampal-like neuronal rebalancing. J A hypothesized neuron-glia circuit model for castle-building behavior. Source data are provided as a Source Data file, and additional related data can be found in Supplementary Data 19–21. Fish artwork in panels I, J is reprinted from iScience, Vol 23/Issue 10, Lijiang Long, Zachary V. Johnson, Junyu Li, Tucker J. Lancaster, Vineeth Aljapur, Jeffrey T. Streelman, Patrick T. McGrath, Automatic Classification of Cichlid Behaviors Using 3D Convolutional Residual Networks, 2020, with permission from Elsevier.