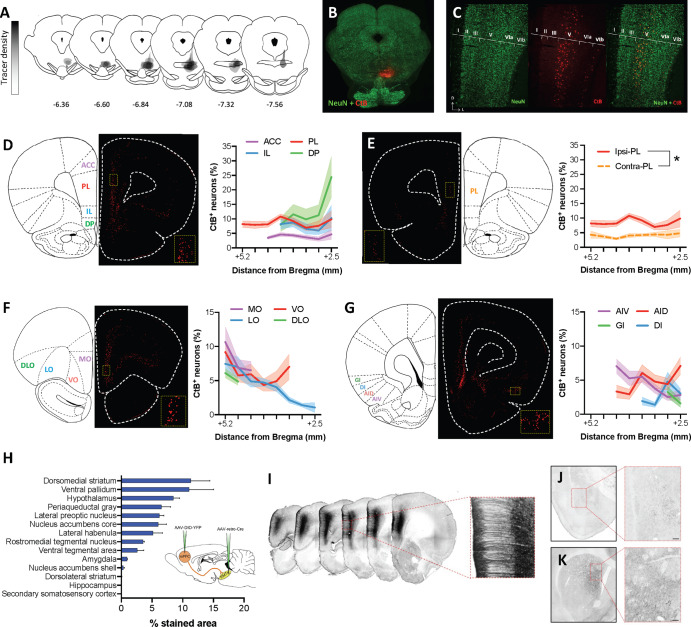
Fig. 1. Anatomical characterization of cortical inputs to the RMTg.
A Map of cholera toxin B (CtB) retrograde tracer injection sites for all animals included in quantification. B Representative injection site image. C Representative high magnification image showing that inputs to the RMTg arise primarily from layer V of the mPFC. D The percent of CtB+ neurons relative to all layer V NeuN+ neurons is relatively consistent across ACC, PL, and IL subregions of the mPFC whereas the density of RMTg-projecting DP mPFC neurons increases substantially at more caudal levels. E Contralateral cortical afferents are substantially less dense than ipsilateral inputs as exemplified by a comparison of RMTg-projecting PL mPFC neurons in both hemispheres. F The density of layer V OFC neurons projecting to the RMTg is similar to that observed in the mPFC with LO inputs diminishing at more caudal levels. G CtB labeling is consistently observed in the AIC, albeit to a lesser degree than that observed in mPFC and OFC. H Quantification of punctate labeling indicative of collateral input from ROIs placed within each brain region in rats prepared using an intersectional dual-virus approach (inset) to fill RMTg-projecting dmPFC neurons with yellow fluorescent protein (YFP). I Representative images showing RMTg-projecting dmPFC neurons filled with YFP following amplification using standard immunohistochemistry. J Representative YFP staining in the amygdala shows relatively sparse collateralization of RMTg-projecting dmPFC neurons in the basolateral nucleus. K Representative YFP staining in the striatum shows dense collateralization in the dorsomedial but not dorsolateral striatum. Scale bar = 100 μm. ACC anterior cingulate cortex, AID dorsal agranular insular cortex, AIV ventral agranular insular cortex, DI dysgranular insular cortex, DLO dorsolateral orbitofrontal cortex, DP dorsopeduncular cortex, GI granular insular cortex, IL infralimbic cortex, LO lateral orbitofrontal cortex, MO medial orbitofrontal cortex, PL prelimbic cortex, VO ventral orbitofrontal cortex.