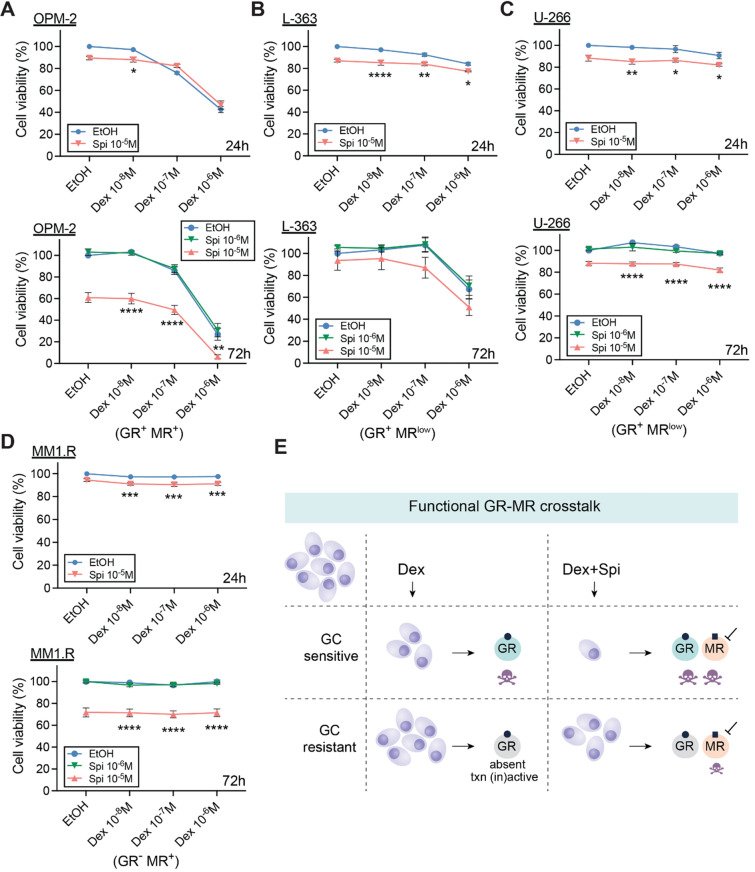
Fig. 3.
The MR antagonist Spi promotes cell killing of MM cells with varying degrees of Dex responsiveness. (A–D) Different myeloma cell lines including (A) OPM-2, (B) L-363, (C) U-266 and (D) MM1.R cells were treated with Dex (10−6 M–10−8 M), Spi (10–5–10−6 M), a Dex-Spi combination or solvent control (set as 100%) for 24 h or 72 h, followed by a CelltiterGlo assay. Biological replicates: OPM-2 (24 h N = 6; 72 h N = 4), L-363 (24 h and 72 h N = 3), U-266 (24 h N = 4, 72 h N = 3) and MM1.R (24 h N = 4, 72 h N = 3). (E) Graphical summary highlighting the existence of a functional crosstalk between GR and MR in MM cells. In GC-sensitive MM cells containing GR, Dex induces MM cell killing, which is further enhanced by the addition of Spi. In GC-resistant cells, where GR is either absent or transcriptionally (in)active, Dex loses its anti-MM activity, while Spi addition does trigger significant MM cell killing. Data information: (A–D) Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 9 using two-way ANOVA with post hoc testing