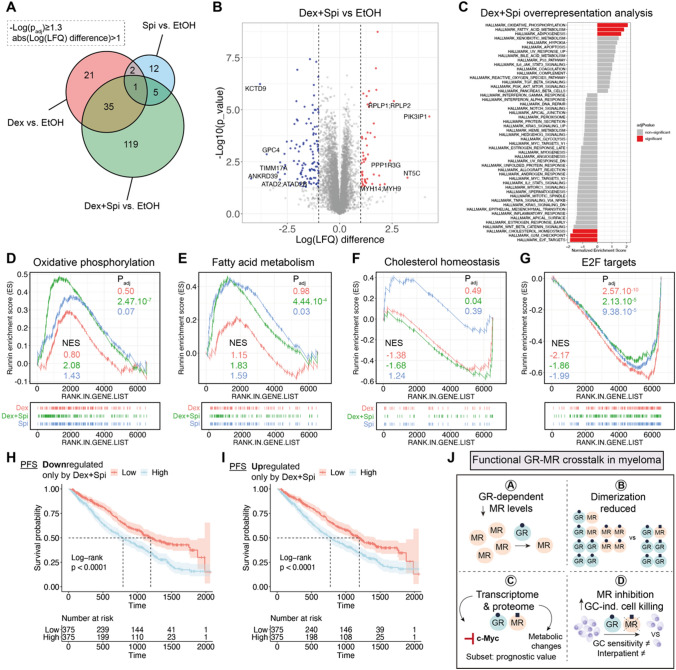
Fig. 7.
Several metabolic pathways are deregulated most by the Dex-Spi combination treatment. (A) MM1.S cells were treated with Dex (10−6 M), Spi (10−5 M), a Dex-Spi combination or solvent control (EtOH) for 24 h, followed by mass spectrometry-based shotgun proteomics. Venn diagram of pairwise comparisons in which significantly regulated proteins (− log(padj) ≥ 1.3) with an abs(log(LFQ difference)) > 1 were considered. (B) Volcano plot depicting the padj (log10 scale) in function of the log(LFQ) in the pairwise comparison Dex-Spi vs EtOH. Significantly regulated proteins − log(padj) ≥ 1.3 are colored in red (log(LFQ) > 1, upregulated) or blue (log(LFQ) < − 1, downregulated); non-significant genes (− log(padj) < 1.3) in grey. (C) GSEA-based overrepresentation analysis for the proteins regulated by Dex-Spi, hereby identifying hallmarks that are significantly (red) or non-significantly (grey) enriched. (D–G) GSEA of single hallmarks, i.e. (D) oxidative phosphorylation, (E) fatty acid metabolism, (F) cholesterol homeostasis or (G) E2F targets, for each pairwise comparison, along with the respective normalized enrichment score (NES) and padj. (H-I) Kaplan–Meier curves of the MMRF patient cohort (N = 750), depicting the survival probability in function of progression-free survival (PFS) for low or high expression of proteins that were uniquely (H) downregulated or (I) upregulated by the Dex and Spi combination. Statistical analyses were performed in R (package survival), using a log-rank test. (J) Several lines of evidence support a crosstalk between GR and MR in MM: A) GCs induce a GR-dependent MR downregulation; B) GR and MR engage in a direct, physiologically relevant endogenous interaction that can be modulated by ligands. Spi was shown to reduce the Dex-induced GR-MR heterodimer levels and abolished Dex-induced MR–MR homodimers. Spi did not impact Dex-induced GR-GR homodimerization; C) Dex and Spi combination gives rise to a differential gene and protein expression profile, in which the inhibition of c-myc and its target genes, and several metabolic pathways are modulated most pronounced by Dex-Spi, respectively. A specific subset of targets may even have prognostic significance; D) MR inhibition enhances GC-induced cell killing in MM cell lines depending on their GC responsiveness and in primary (heterogeneous) MM cells depending on the disease stage