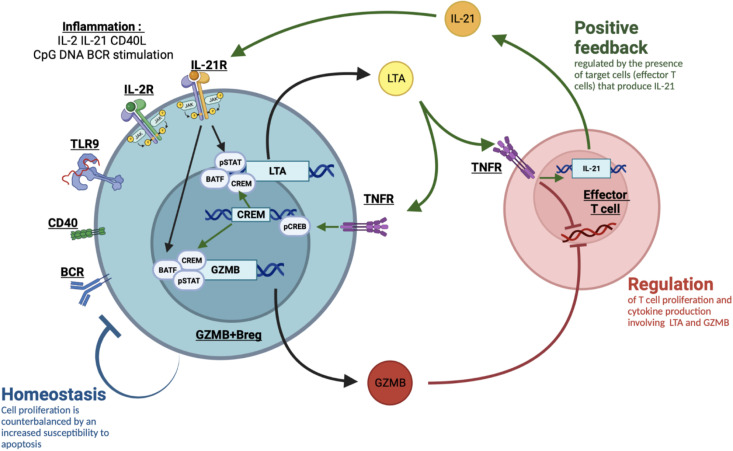
Figure 7.
Proposed model of LTA/GZMB interaction in GZMB+Bregs. Upon inflammatory conditions involving IL-2, IL-21, CD40L, CpG DNA and BCR stimuli, B cells differentiate into a GZMB+ regulatory B cell phenotype. IL-21 stimulation is a potent activator of both pSTAT1, pSTAT3 and BATF. Among the targets of pSTATs, we found LTA, that is upregulated in GZMB+Bregs. LTA binding on its receptors TNFR1 and TNFR2 has multiples effects. First, it directly inhibits T cell proliferation. It also increases IL-21 production in T cells thus involving positive feedback on the GZMB+Bregs that express higher level of IL21R. This loop requires the presence and the functional activity of the target T cells to produce IL-21. Last, in the GZMB+Bregs, LTA binding on TNFR activates CREM transcription through CREB phosphorylation. CREM is a transcription factor associated to the promoters of LTA and GZMB, thus associated with LTA and GZMB expression on the GZMB+Bregs. GZMB is also a direct target of BATF. This leads to the suppressive properties of GZMB+Bregs through GZMB and LTA. To counterbalance the positive feedback, GZMB+Bregs have increased apoptosis susceptibility.