Figure 1. Experimental design, analysis plan, and quality control: adult mouse hippocampus and its excitatory neurons.
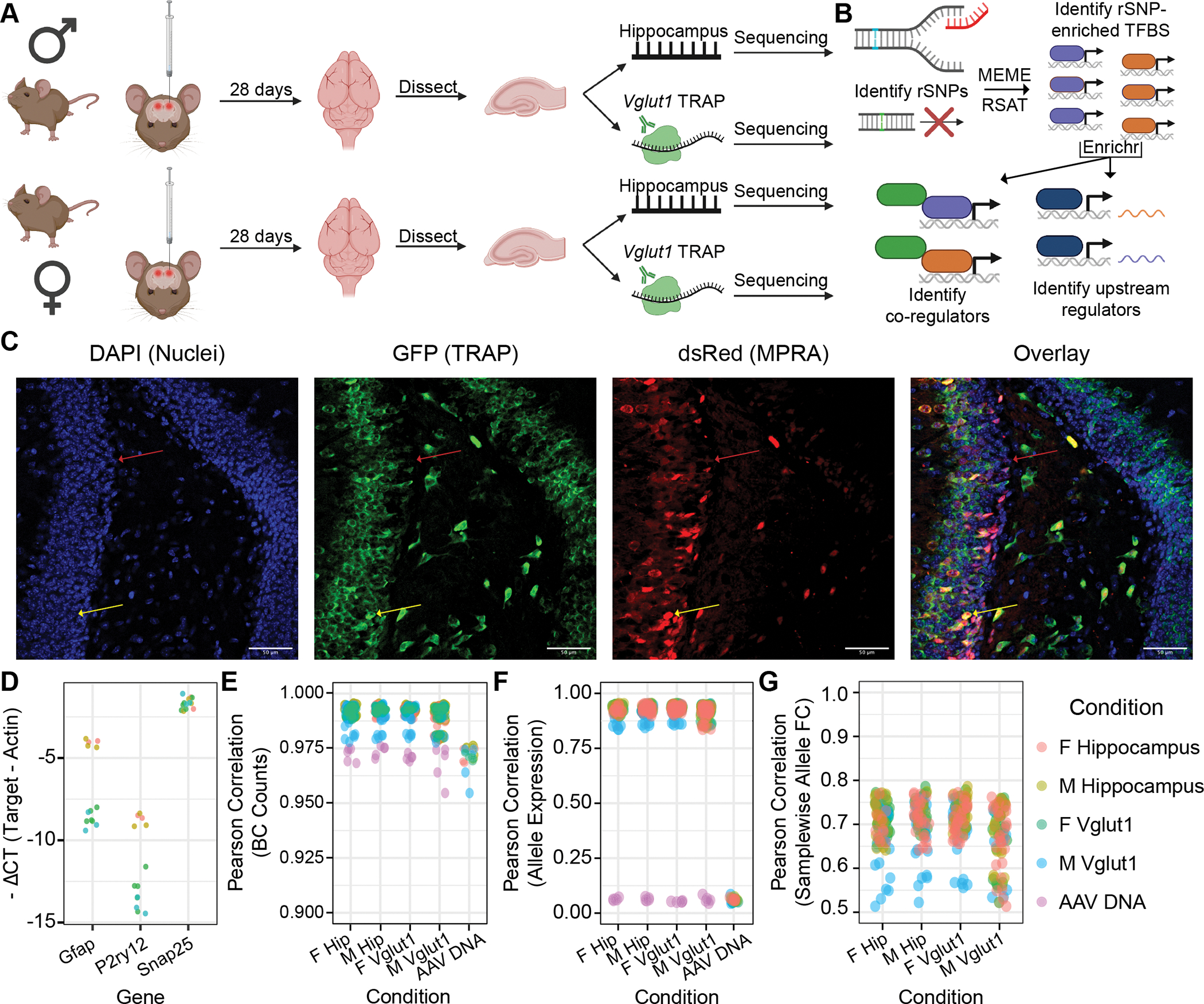
(A) Adult male and female C57BL/6J mice received bilateral stereotactic injections into the hippocampus delivering the AAV9-packaged MPRA. TRAP yielded two RNA fractions per sample: “input” (total hippocampal) and TRAP (Vglut1+). (B) Analyses identified regulatory SNPs (rSNPs), transcription factor (TF) binding sites (TFBSes) enriched at rSNPs, shared protein interactors among these TFs, and shared regulators of these TFs’ expression. (C) IF of Vglut1-TRAP mouse hippocampus 28 days after MPRA-AAV9 delivery, illustrating strong TRAP (GFP) co-expression with dsRed reporter, confirming RNA from the latter is present in the cell type of interest. (D) qPCR confirmed depletion of glial genes (Gfap, P2ry12) and modest enrichment of excitatory neuron marker Gria1 in Vglut1+ RNA. (E) Barcode count correlations between replicates. Each point represents the cross-correlation between one sample of the type on the x-axis and one of the color-coded type. (F) Correlation of mean barcode expression between replicates. (G) Correlation of samplewise allelic differences in expression. PCC: Pearson correlation coefficient (or Pearson’s r).
