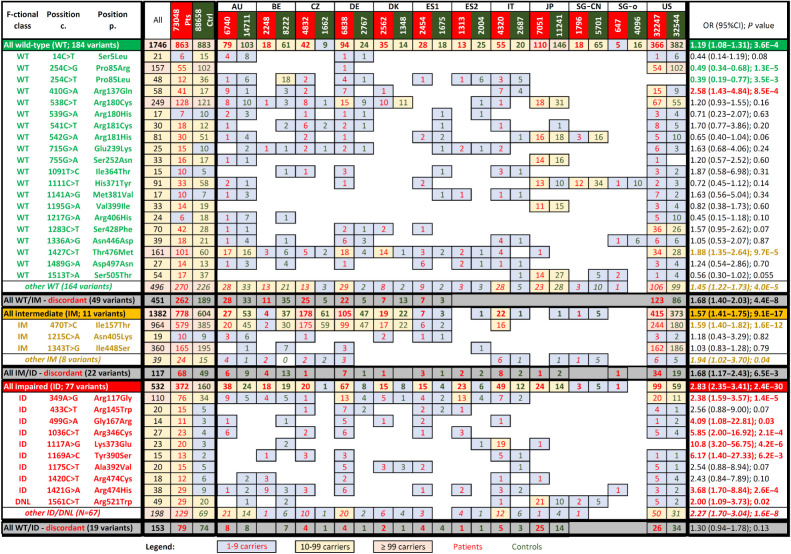
Figure 5.
Presence of analyzed CHEK2 missense variants categorized according to the functional assays in patients with breast cancer (BC pts; red numbers) and matched controls (dark green numbers). The association with breast cancer risk (odds ratio; OR) were calculated for prevalent variants having ≥10 carriers among patients or controls, respectively. Colors of the numbers in the last column highlight significant association with moderate-or-higher risk (red; OR > 2), low risk (OR < 2), protective variants (green) or variants without significant impact on breast cancer risk (black). Gray rows display variants that were discordant in the kinase assays. DNL, variants that do not localize into the nucleus.