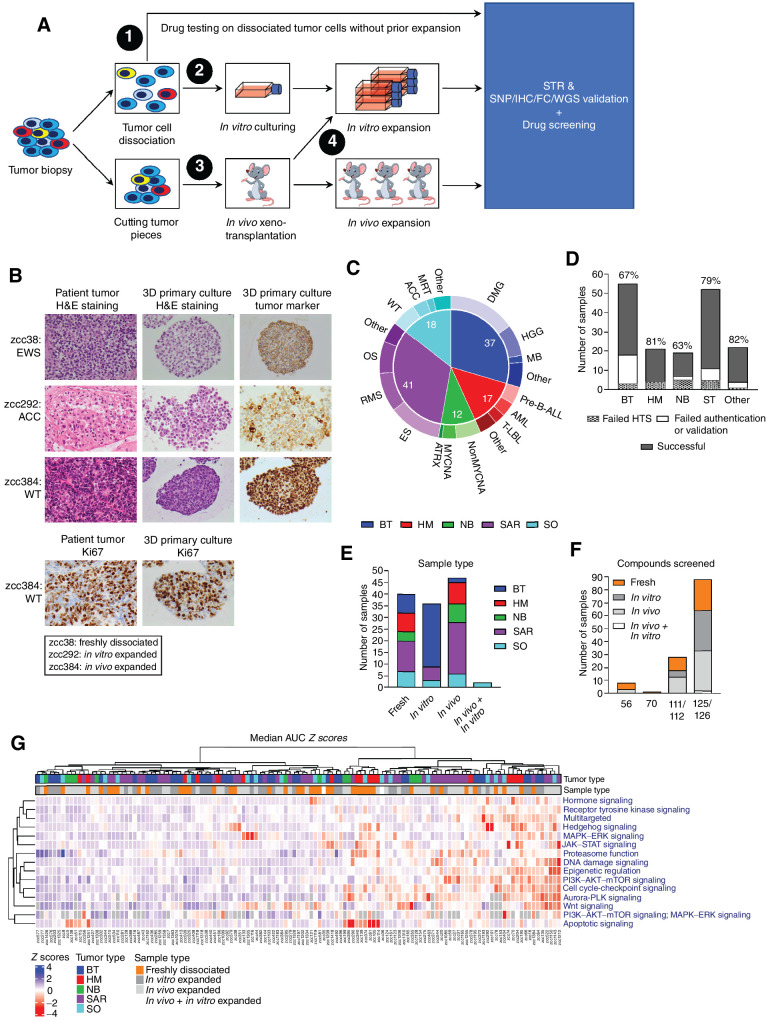
Figure 1.
Drug response profiles are independent of tumor cell expansion. A, Workflow for in vitro HTS on tumor cells derived from patients enrolled in the ZERO childhood cancer precision medicine program. HTS is performed on freshly dissociated tumor cells or tumor cells expanded by in vitro culturing and/or in vivo growth. Samples are authenticated by STR profiling and validated by at least one of the following methods: SNP array, IHC, flow cytometry (FC) or, for screens on freshly dissociated tumor cells only, WGS. B, Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of representative patient tumor samples (left) and matching 3D primary cultures (middle), and IHC of tumor markers in the 3D primary cultures (right). Tumor markers used: CD99 for Ewing sarcoma sample zcc38, inhibin for adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC) sample zcc292, and WT1 for Wilms tumor (WT) sample zcc384. Bottom images show Ki67 staining results for matching tumor biopsy and 3D primary culture of WT zcc384. C, Cancer types and subtypes with successful in vitro HTS (N = 125). D, Number of patient-derived samples for main types of pediatric cancer that underwent in vitro HTS. Percentages indicate samples for which HTS, authentication by STR profiling and validation by SNP array profiling, IHC, flow cytometry, or WGS was successful. E, Successful in vitro HTS on freshly dissociated and expanded samples highlighted by cancer types. F, Number of samples screened by different sized libraries and the associated methodology used to generate the samples for HTS (i.e., fresh dissociation of tumor cells or in vitro and/or in vivo expansion of tumor cells). G, Heatmap of the targeted drug response profiles across the 125-sample cohort. Drug response profiles were established by calculating the median AUC Z scores for targeted drugs grouped according to MOA. Median AUC Z scores are represented by a color scale from blue (resistant) to red (sensitive). MOAs and tumor samples are ordered by unsupervised hierarchical clustering. Top annotations indicate tumor type and type of sample. Tumor type key: brain tumors (BT), hematologic malignancies (HM), neuroblastoma (NB), sarcoma tumors (SAR), solid other (SO). Cancer subtype key: diffuse midline glioma (DMG), high-grade glioma (HGG), medulloblastoma (MB), B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Pre-B-ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), T-lymphoblastic leukemia (T-LBL), non-MYCN-amplified (NonMYCNA), MYCN-amplified (MYCNA), alpha thalassemia/mental retardation syndrome X-linked (ATRX), Ewing sarcoma (ES), rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS), osteosarcoma (OS), Wilms tumor (WT), adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC), malignant rhabdoid tumor (MRT).