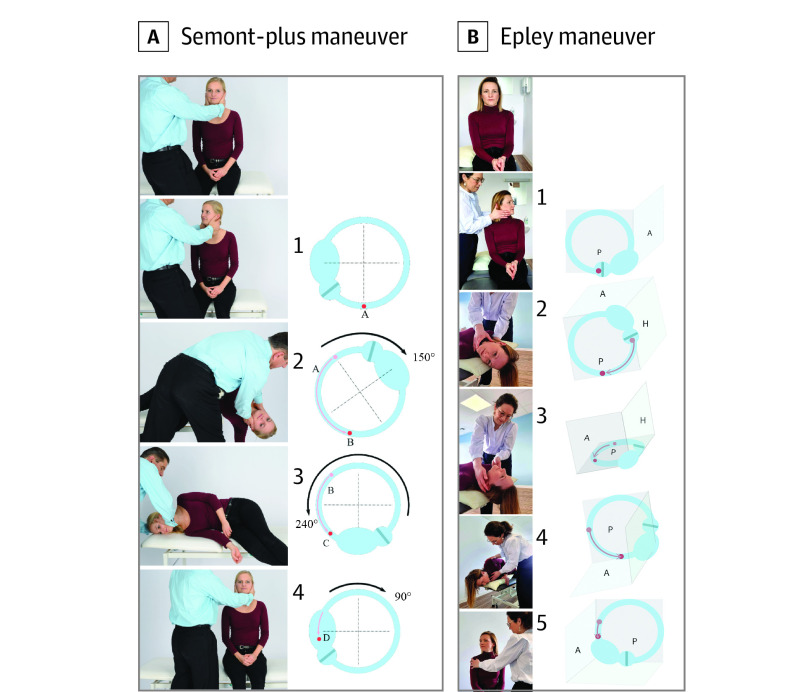
Figure 1. Schematic Drawing of the Movement of the Otoconia of the Semont-plus Maneuver and Epley Maneuver for Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo of the Left Posterior Canal.
A, The Semont-plus maneuver includes the upright position with (1) turning of the head by 45° toward the nonaffected side; (2) movement of the body by 150° toward the affected side, which moves the otoconia further in the direction in which they should move (A toward B); (3) and since the clot is beyond the vertex (B toward C), the movement of body by 240° moves the clot into the direction (4) of the vestibulum (position D of the otoconia). B, The Epley maneuver includes upright position and (1) rotation of the head 45° toward the affected ear; (2) movement of the body backward so that the head is in a hanging position below the earth horizontal; (3) rotation of the head 90° toward the nonaffected ear; (4) rotation of the whole body downward so that the patient faces the floor and their affected ear is pointing toward the ceiling; and (5) going into the upright position while keeping a rotation of the head 45° toward the nonaffected ear, and turning the head back to the neutral position at the end. A indicates anterior semicircular canal; H, horizontal semicircular canal; and P, posterior semicircular canal.