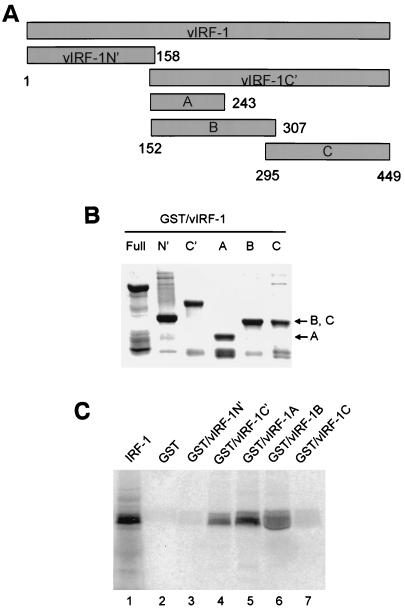
FIG. 4.
Mapping of vIRF-1 interaction domain. (A) Positional scheme of vIRF-1 deletion mutants. Numbers correspond to amino acid boundaries of respective fragments. (B) Coomassie blue-stained gel illustrating the purity and size of the respective GST–vIRF-1 fusion fragments. (C) In vitro interaction between IRF-1 and different vIRF-1 fragments as detected by pull-down assay. 35S-labeled IRF-1 input (20%) and its binding to GST beads are shown in lanes 1 and 2, respectively. IRF-1 was pulled down by GST–vIRF-1C′ (lane 4) and not by GST–vIRF-1N′ (lane 3). Both GST–vIRF-1A (lane 5) and GST–vIRF-1B (lane 6) fragments actively bound IRF-1, while no IRF-1 binding was detected with GST–vIRF-1C fragment (lane 7).