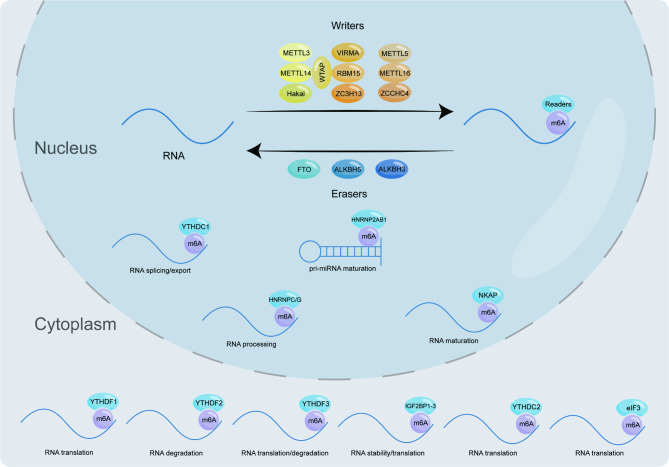
Fig. 1.
Regulation of m6A modification. The writers and erasers of m6A are responsible for regulating the methylation level of related RNA. Then, various m6A readers can recognize and combine with m6A modified RNA to regulate gene expression. METTL3, Methyltransferase-like 3; METTL14, Methyltransferase-like 14; WTAP, Wilms tumor 1-associated protein; RBM15, RNA binding motif protein 15; VIRMA, Vir-like m6A methyltransferase associated; ZC3H13, zinc finger CCCH-type containing 13; METTL16, Methyltransferase-like 16; METTL5, Methyltransferase-like 5; ZCCHC4, zinc finger CCHC-type containing 4; FTO, Fat mass and obesity-associated protein; ALKBH3, ALKB homologue 3; ALKBH5, ALKB homologue 5; YTHDF1, YTH N6-Methyladenosine RNA Binding Protein 1; YTHDF2, YTH N6-Methyladenosine RNA Binding Protein 2; YTHDF3, YTH N6-Methyladenosine RNA Binding Protein 3; YTHDC1, YTH Domain Containing 1; YTHDC2, YTH Domain Containing 2; HNRNPA2B1, Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2B1; HNRNPAC/G, Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C/G; HNRNPR, Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein R; IGF2BP1-3, Insulin Like Growth Factor Binding Protein 1–3; NKAP, NF-κB activating protein; eIF3, Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3