Table 2.
The basic equivalent electrical circuit models (derivations and modifications of) which are commonly used in the modeling of plant EIS measurements.
| Equivalent electrical circuit | Description |
|---|---|
|
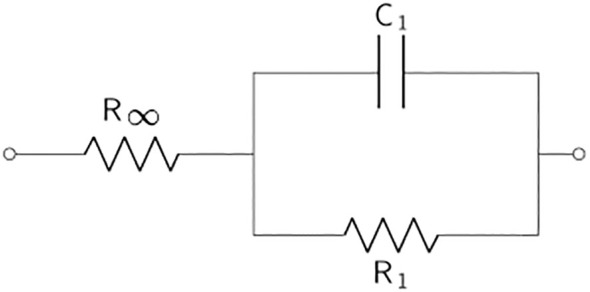
The simple Voigt or Debye circuit without inductor. The single dispersion Cole model proposed by Cole (1940) can be seen as the fractional elaboration of Voigt circuits, where a CPE replaces the capacitor. This is one of the oldest fractional circuit models and is often used to model biosystem impedance spectra. In that case, R ∞ is the high-frequency resistance, and R 1 + R ∞ is the low-frequency resistance. A drawback is the limited biological interpretability. |
|
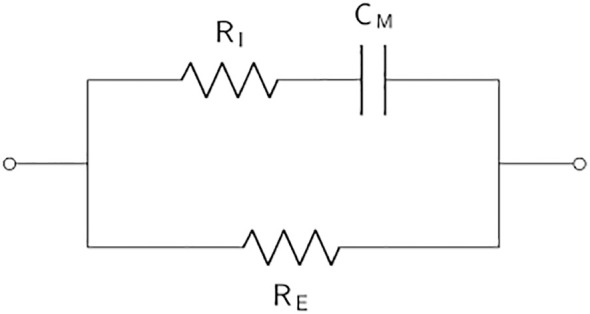
The single shell model (Toyoda and Tsenkova, 1998), also called the simplified Hayden model (Hayden et al., 1969). R E is the extracellular resistance of the apoplastic fluid, R I is the intracellular resistance, and C M is the capacitance of the cell membrane. The name of the model was coined by Zhang et al., contrasting it with their proposed double shell model (Zhang and Willison, 1992). |
|
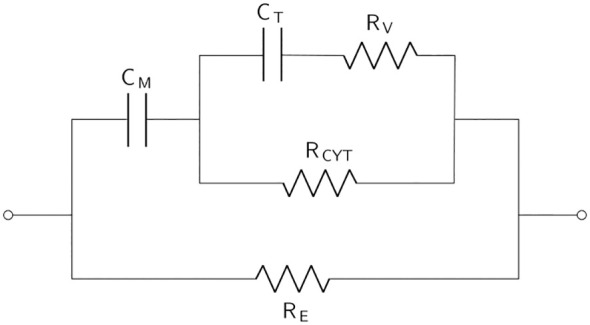
The double shell model proposed by Zhang and Wilson (1991). C M is capacitance of the cell membrane, C T is the capacitance of the tonoplast, R CYT is the cytoplasmic resistance, R V is the vacuolar resistance, and R E is the extracellular resistance. In some works, R V is referred to as the resistance of the cell wall (Harker and Maindonald, 1994). |
