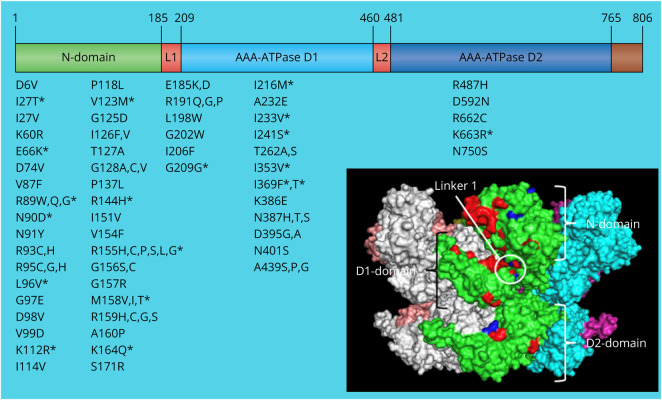
Figure 1. Location of the Novel Mutations in the VCP Gene and Protein.
Scheme of the location of all the variants described in the VCP gene and protein structure. The VCP protein contains 806 amino acids and is constituted by an N-terminal domain involved in the cofactor and ubiquitin-binding function, a D1 domain involved in the assembly of VCP homohexamer, a D2 domain responsible for the major ATPase activity, and the C-terminal domain involved in nuclear localization by interacting with other proteins. The N-domain and D1 domain are connected by N-D1 linker (L1), and the D1and D2 domains are connected by flexible D1-D2 linker (L2). All variants are listed underneath the domain affected; those with an asterisk are considered novel. The black square contains a 3D render of a VCP hexamer. Each subunit is independently colored. The positions of previously reported pathogenic residues are denoted in red and the novel reported variant residues in blue within a single green monomer. VCP = valosin-containing protein.