Figure 3.
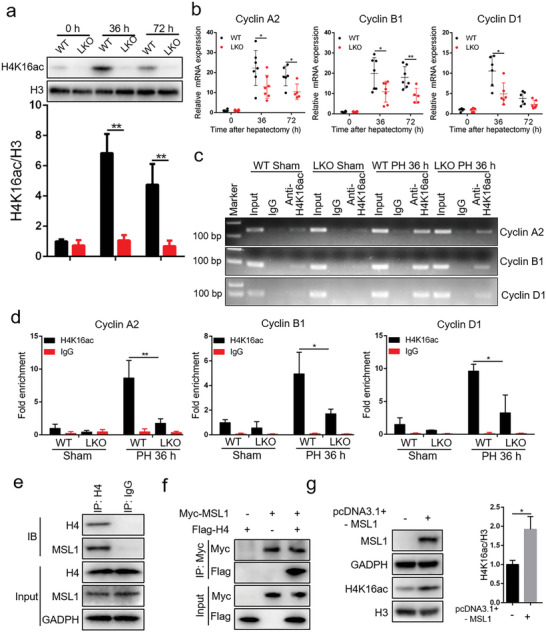
MSL1 regulates cell cycle genes through H4K16 acetylation. a) Immunoblot analysis of liver tissues lysates prepared from WT and LKO mice at 36 and 72 h after partial hepatectomy (PH) using the indicated antibodies. Lower panel show the quantification of protein levels H4K16ac by densitometric analysis and normalization versus loading control (n = 3). b) qRT‐PCR analysis of Cyclin A2, Cyclin B1 and Cyclin D1 mRNA expression in the regenerating liver (n = 5–7 mice per group). c,d) ChIP‐PCR (c) and ChIP‐qPCR (d) assay of H4 K16ac level on Cyclin A2, Cyclin B1, and Cyclin D1 promoters using chromatin solutions prepared from WT and LKO mice at 36 h post PH or the sham procedure (n = 3 mice per group). e) Coimmunoprecipitation analysis of MSL1 and H4 in liver tissues from WT mice. f) HEK293T cells were transfected with Myc‐MSL1‐encoding plasmids and with or without Flag‐H4 plasmids, followed by culturing for 24 h. Coimmunoprecipitation analysis was performed. g) Hep1‐6 cells were transfected with plasmids for MSL1 or control vector for 24 h. Immunoblot analysis using the indicated antibodies. Right panel show the quantification of protein levels H4K16ac by densitometric analysis and normalization versus loading control (n = 3). The data were expressed as means ± SD. Significant difference was presented at the level of * p < 0.05 and ** p < 0.01 by two‐tailed Student's t‐test.
