Figure 3.
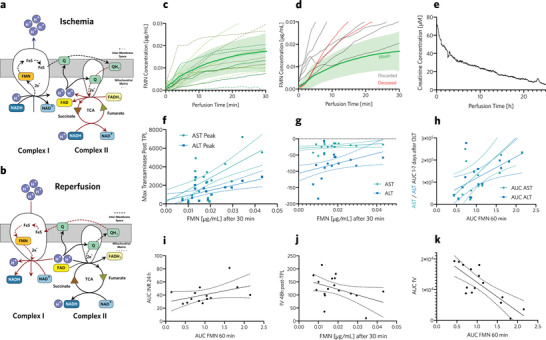
Mitochondrial damage: Respiratory chain during ischemia a) and reperfusion b). c) Real‐time measurements of change in FMN concentration in perfusate during HOPE of grafts that were transplanted, indicating progress of ischemic reperfusion injury in real‐time. Mean FMN concentration (green bold line) and 95% confidence region (green shaded area) of successfully transplanted grafts. d) Real‐time FMN concentration during HOPE of discarded grafts (gray lines), and grafts transplanted into patients who deceased after transplantation (red lines). Mean FMN concentration (green bold line) and 95% confidence region (green shaded area) of successfully transplanted grafts. e) Blood creatinine concentration, measured during normothermic liver perfusion. f) Peak inflammation marker concentrations after a transplant, compared to FMN concentrations (µg mL‐1), 30 min after HOPE began. Higher FMN concentrations during HOPE correlated with peak transaminase levels after transplantation, which indicated increased hepatic inflammation. g) Exponent of transaminase decay compared with FMN concentration at 30 min of HOPE. Lower FMN concentrations during HOPE correlated with faster decay of transaminase levels indicating more rapid patient recovery. h) Area under the curve (AUC) compared between AST, ALT (days 1–7 after transplant) and FMN within the first 60 min of HOPE. This correlation shows that patients with grafts with lower FMN concentrations were exposed to less hepatic inflammation after liver transplantation. i) Correlation of AUC of released FMN during the first 60 min of HOPE and INR during the first 24 h after liver transplant. As a reference, an average INR of 1 during the first day would be equivalent to an AUC INR 24 h of 24. Hence, grafts with higher FMN values exhibited increased INR after transplantation, thereby indicating slower recovery of hepatic function. j) AUC of factor V within days 1–7 after transplant compared to AUC of FMN within the first 60 min of HOPE. This showed that patients with low FMN grafts had improved coagulation factor synthesis after transplantation, indicating better organ function. k) Interpolated fV value, 48 h after transplantation, showing increased liver function for patients with low FMN grafts.
