Figure 7.
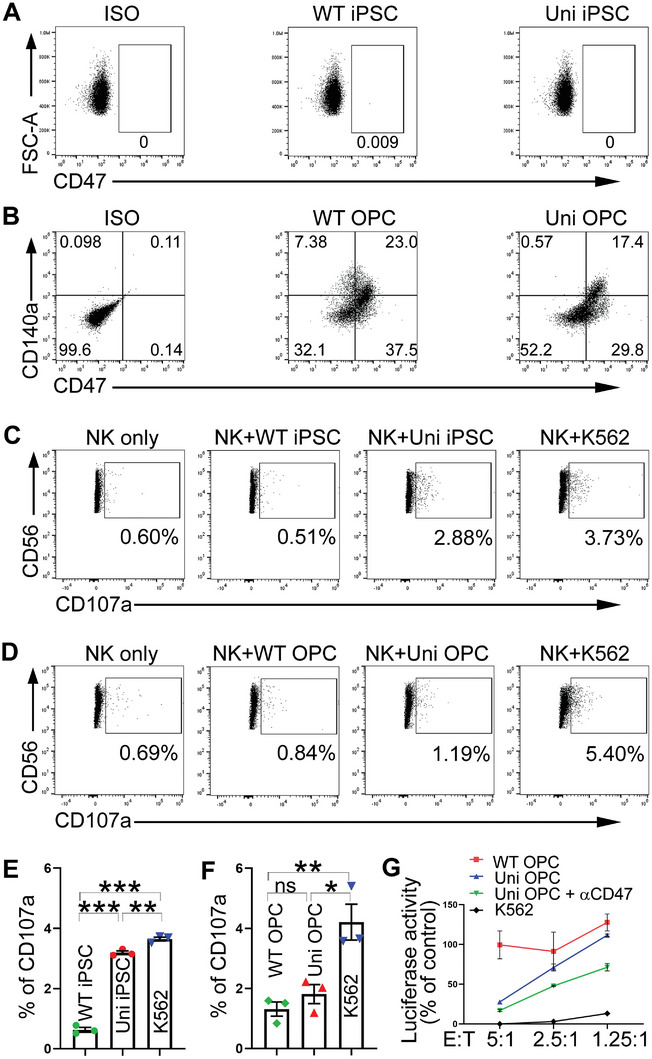
The uni OPCs partly evade NK response. A) Both the WT and the uni iPSCs didn't express CD47 based on the Flow cytometry analysis. B) Both the WT and the uni OPCs expressed CD47. Flow cytometry analysis of the WT or the uni OPCs stained with antibodies for CD140a and CD47. C–F) The uni OPCs, not uni iPSCs were able to evade the NK response. The WT or uni iPSCs and OPCs were co‐cultured with NK cells isolated from allogenic PBMC. The degranulation assay by flow cytometry analysis of CD107a expression to assess NK cell activation is show in panels C and D. The K562 cells were included as the positive control and the NK cells only as the negative control. Quantification from three experiments is shown in panels (E) and (F). n = 3 biological repeats. G) NK cells exhibited reduced lytic activity toward the uni OPCs, and this suppression was relieved partially by the treatment with a CD47 neutralizing antibody (αCD47). The luciferase reporter‐bearing WT or uni OPCs or the K562 cells that were included as a positive control were co‐cultured with NK cells for 48 h and the luciferase activity was measured. The uni OPCs exhibited much less lysis than K562 cells as revealed by the higher luciferase activity in the uni OPC than that of the K562 cells. The CD47 neutralization antibody increased NK‐mediated lysis of the uni OPCs as revealed by the reduced luciferase activity upon αCD47 treatment (uni OPC + αCD47). Error bars are SE of the mean. ns, not significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 by one‐way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparisons test for panels (E) and (F).
