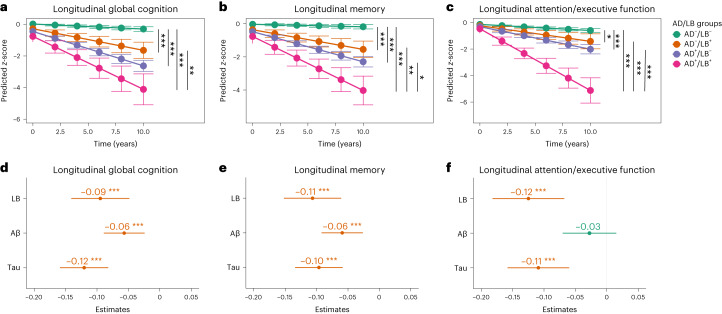
Fig. 3. Independent effect of AD/LB groups and LB, Aβ and tau pathologies on longitudinal cognitive performance.
a–c, Significant effects (two-sided) were examined with LME models focusing on the interaction of AD/LB group × time, adjusted for age, sex and education. a,d, Longitudinal global cognition. b,e, Longitudinal memory. c,f, Longitudinal attention/executive function. d–f, Interaction time × all three pathologies (binarized) was used in the same model to examine the independent effects of each pathology on cognitive progression while adjusting for age, sex and education. Outcomes were z-scored cognitive tests. d–f, Red indicates significant association between pathology and worse cognitive decline. The effect of LB on clinical outcomes with/without adjusting for Aβ and tau is shown in Extended Data Table 3. a–c, Estimated marginal means and 95% CI of means obtained from LME models by AD/LB group. d–f, Dot/center indicates the interaction estimate of time × pathology; error bars 95% CI. In total, 941 participants were AD–/LB–, 74 AD–/LB+, 147 AD+/LB– and 20 AD+/LB+; 94 were LB+, 304 Aβ+ and 195 tau+. Statistical analyses with corrections for multiple comparisons are shown in Supplementary Fig. 3 (all significant differences/associations were still significant after correction). Missing data shown in Supplementary Table 2. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (two-sided).