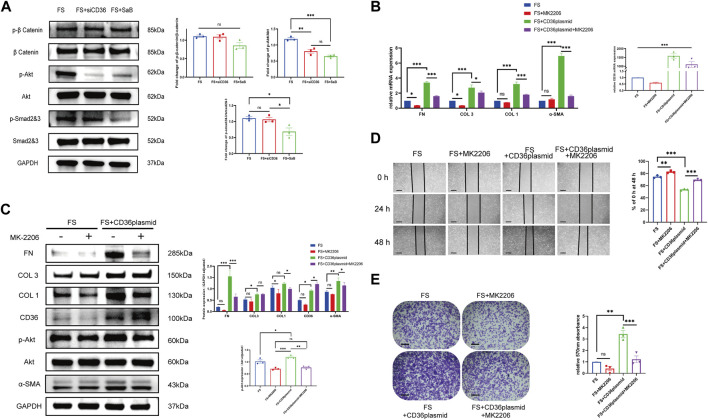
FIGURE 6.
CD36 promotes pathologic synovial fibroblast-induced fibrosis in FS through the PI3k-Akt pathway. (A) The expression of p-Akt/Akt, as well as several key molecules in other classic fibrosis-related pathways including the TGF-β1/SMAD pathway and the WNT/β-catenin pathway, was examined in synovial fibroblasts treated with siRNA or SaB. (B,C) Western blotting and qRT-PCR results showed that COL 1, COL 3, FN and α-SMA along with Akt phosphorylation was significantly upregulated in FS synovial fibroblasts after the overexpression of CD36, and this trend was reversed by Akt inhibitor, MK2206. (D,E) Cell adhesion test and Wound-healing suggested that MK2206 inhibited the enhanced fibrosis-related functions in synovial fibroblasts caused by the overexpression of CD36. Scale bar: 50 μm *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.