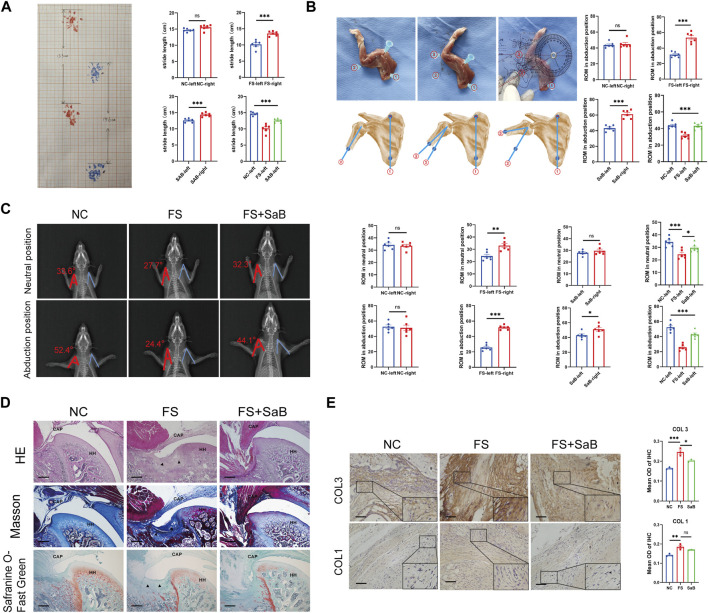
FIGURE 7.
SaB blocks the progression of pathologic fibrosis of frozen shoulder in vivo. (A) Gait analysis by measuring the stride length on a grid paper. Stride length is defined as the longest distance between the front and rear paws. (B) Evaluation of the shoulder ROM. The angle between the scapular medial border (line 1) and humerus shaft (line 2 or 3) was measured, and the ROM was calculated by subtracting the angle in a maximally adducted position from the angle in a maximally abducted position. (C) The neutral and abduction positions’ X-ray films were collected using a flatbed scanner. Consider the axis of the humerus and the lateral edge of the scapula as the two sides of an angle with the humeral head’s center as the vertex. (D) The capsular areas were increased in the left immobilized shoulder in groups B and C, while group C showed a significantly smaller capsular area than that of group B. Besides, the amount of inflammatory cells observed in group C was significantly lower than that in group B, but higher than in group A, although not statistically significant. Black arrow: Deposition of collagen. HH: humeral head; CAP: capsule of joint. Scale bar: 100 µm. (E) Higher expression of COL 1 and COL 3 in capsule was observed in group B than the other 2 groups, while no significant difference was found between group A and C. Scale bar: 50 μm *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.