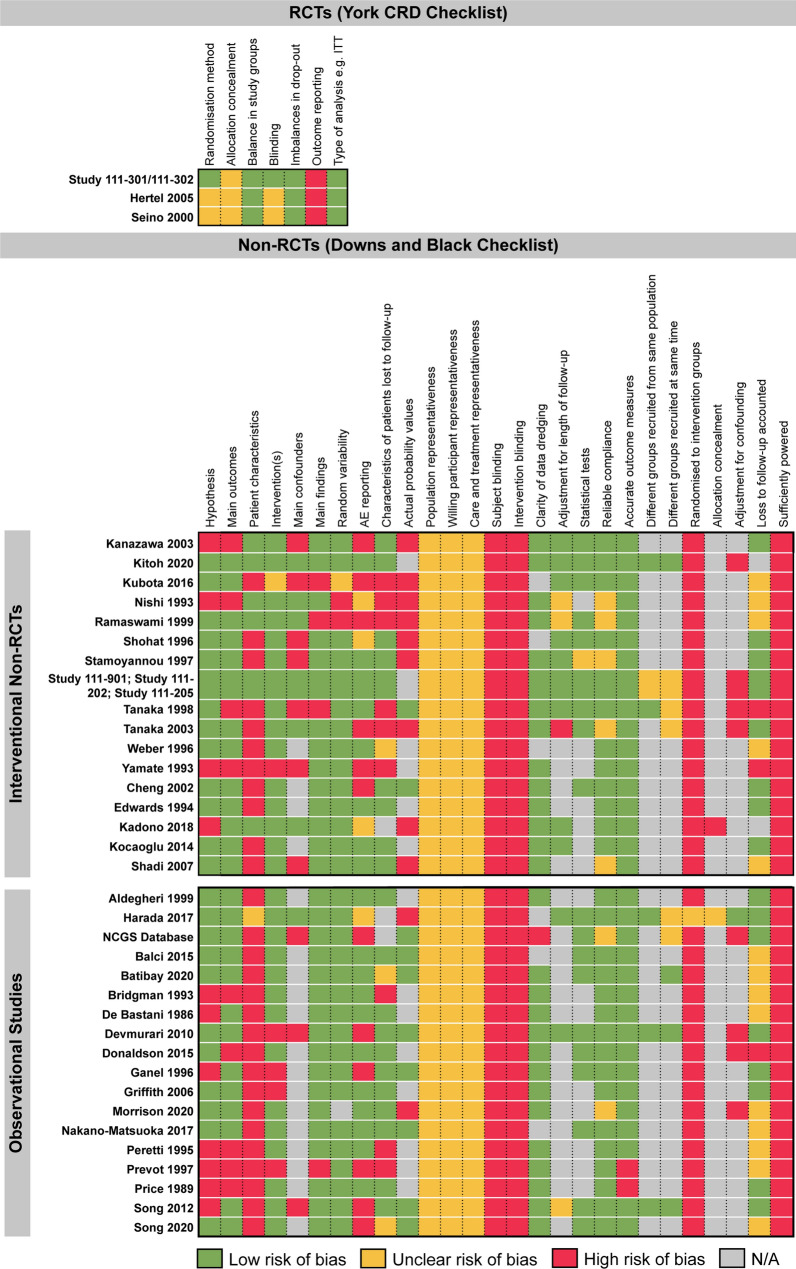
Fig. 6.
Summary of quality assessments. Summary of quality assessment scoring for different study designs reporting clinical evidence. RCTs were assessed using the York CRD tool [32]; non-randomised interventional studies and observational studies were assessed using the Downs and Black checklist [33]. Separate quality assessments were not performed for the extension studies of Study 111-301 and 111–202. All three RCTs used ITT analysis and reported similar baseline characteristics between arms; however, none provided details on allocation concealment. Of the 17 interventional non-RCTs, the majority clearly described the measured outcomes, stated the objectives and provided estimates of the random variability in outcome data. However, the representativeness of patients to the entire population of children with achondroplasia from which they were recruited was unclear. Of the 18 observational studies, 11 stated the objectives clearly, 13 described the main outcomes to be measured, and 14 clearly described the intervention of interest. However, the characteristics of patients were not described clearly by any study. AE adverse event, CRD Centre fpr Reviews and Dissemination, ITT intention to treat, NA not applicable, RCT randomised controlled trial