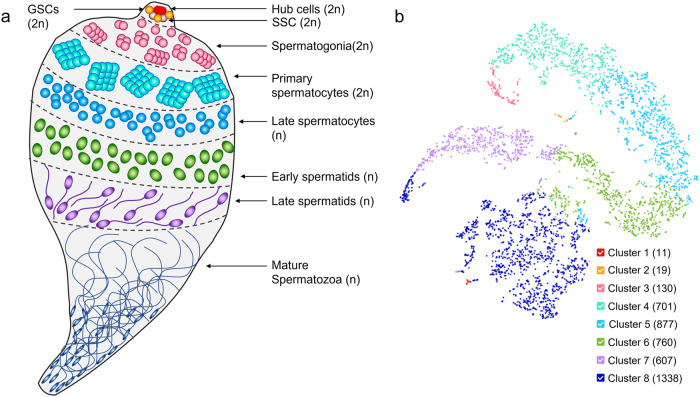
Fig. 1. A single-cell population of the Anopheles male germline.
a Schematic of the different cell types of the male germline and their progression through spermatogenesis from diploid (2n) to haploid (n) cells. In the apical region of the testes the hub cells and somatic stem cells (SSC), together with the germline stem cells (GSCs), form the stem cell niche. GSCs divide to give rise to two daughter cells: one remaining a stem cell and the other developing into a primary spermatogonia cell. Spermatogonia undergo rounds of mitosis to produce primary spermatocytes. Meiotic division then gives rise to haploid spermatocytes which eventually develop into maturing spermatids and spermatozoa. b t-SNE dimensionality reduction plot of single-cell RNA sequencing dataset from A. gambiae testes. Each dot represents a cell which is mapped according to transcriptional similarities with neighbouring cells. Cells are colour coded by K-means cluster with the number of cells in each cluster shown in parentheses.