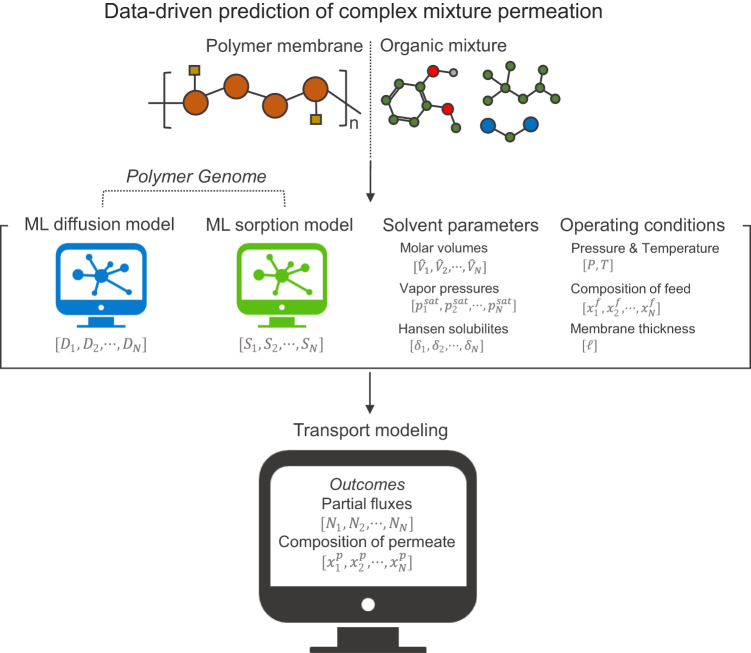
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of data-driven transport modeling framework.
Polymer structures and solvent mixtures are converted to simplified molecular-input line entry system (SMILES) strings and used as inputs for machine-learning algorithms designed to relate polymer-solvent structure to solvent diffusivities (D) and solubilities (S) within polymer membranes. These parameters – in addition to the various physicochemical properties of the solvents (e.g., molar volumes (), vapor pressures (psat), Hansen solubility parameters (δ)) at the desired operating conditions (e.g., pressure (P), temperature (T), composition of the feed mixture (x f), membrane thickness ()) – are then used as inputs into an N-component Maxwell-Stefan model that outputs a vector of fluxes (N) and compositions (x p) for each component permeating through the membrane.