Extended Data Figure 10. Examples of haplotype scaffolding by Rukki in the HG002 genome.
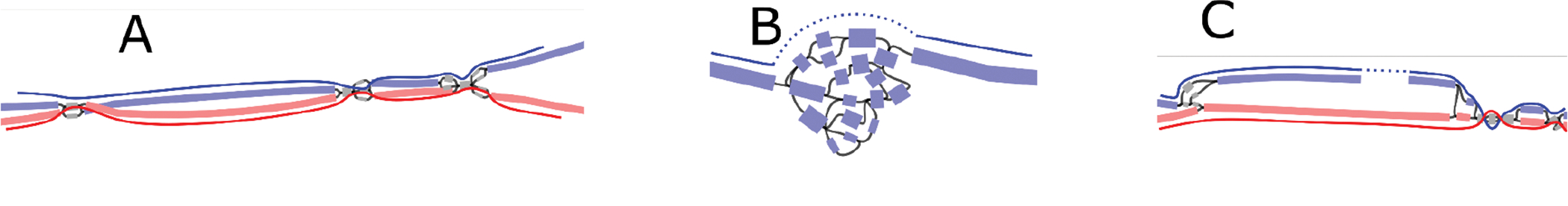
The nodes are colored according to their haplotype assignments. Nodes with at least 100 total markers where 90% of the markers agree are colored: red for maternal, blue for paternal. Nodes with less than 100 markers are colored gray for unassigned. The haplotype paths are marked with solid curves with dotted curves for gaps. (A) A well behaved genomic region consisting of phased heterozygous bubbles, homozygous nodes, and spurious nodes caused by sequencing errors. Where possible, Rukki connects the nodes attributed to the same haplotype across the homozygous regions, producing two phased unitigs without gaps. (B) A tangle within one haplotype. Rukki scaffolds across the tangle (dotted line), reporting an estimated size of the tangled region. (C) A gap in the paternal haplotype. Rukki uses haplotype assignments and the topology of the graph to scaffold across the gap (dotted line), and estimates the size of the gap based on the size of the paired haplotype.
