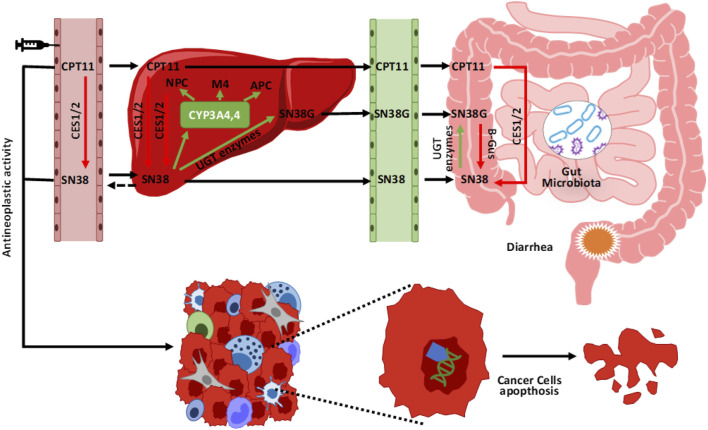
FIGURE 4.
Metabolism and elimination of irinotecan (CPT11). Once injected, irinotecan is activated by some esterases (CES 1/2) into its active metabolite (SN38). After its anticancer action, it is again conjugated in the liver into an inactive compound ready to be eliminated (SN38G) mainly through the intestine and faeces. In its colonic passage, the presence of bacterial groups with enzymatic b-glucuronidase activity, reactivate the compound (SN38) again, effectively increasing its concentration and the risk of associated toxicity (e.g., mucositis).