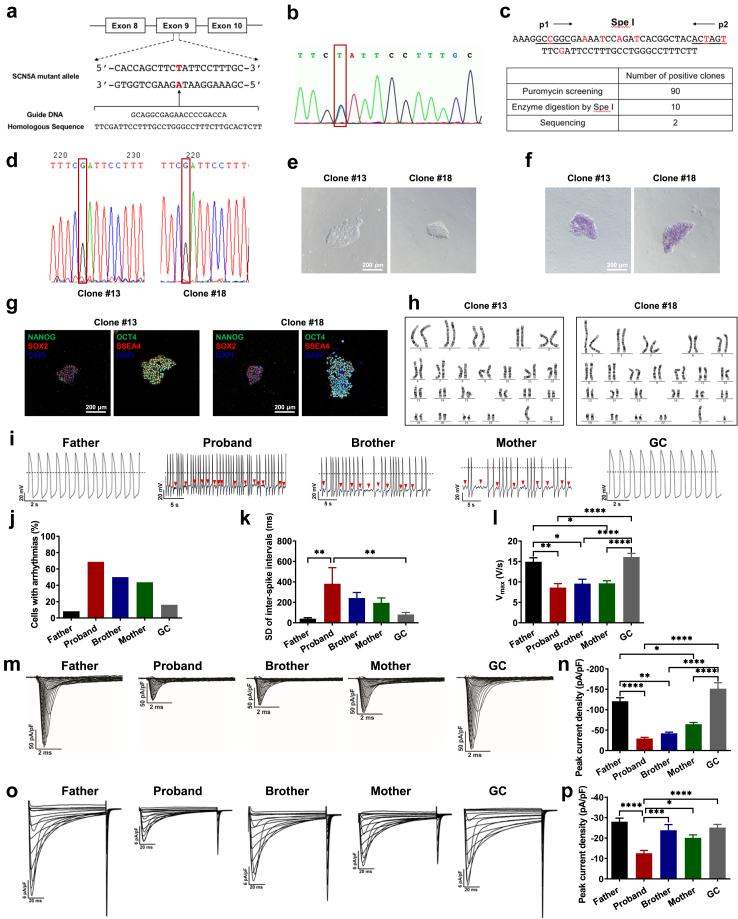
Fig. 5.
Rescuing BrS phenotypes of proband iPSC-CMs by genetic correction of SCN5A D356Y. a. Strategy of correcting SCN5A D356Y mutation. The mutation site is marked in red. b. Confirmation of the existence of SCN5A D356Y mutation in proband iPSCs. c. Spe I restriction digestion of PCR products before and after gene correction, and summary of number of positive clones after puromycin screening (90 positive clones), enzyme digestion by Spe I (10 positive clones) and DNA sequencing (2 positive clones), respectively. d. DNA sequencing demonstrating the correction of 1066G > T (D356Y) mutation, and two gene-corrected clones were obtained (clone #13 and clone #18). e. Typical morphology of GC iPSCs. Scale bar, 200 μm. f. Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) staining of GC iPSCs. Scale bar, 200 μm. g. Pluripotent staining of GC iPSCs using NANOG (green), SOX2 (red), OCT4 (green) and SSEA4 (red). DAPI indicates nuclear staining (blue). Scale bar, 200 μm. h. Representative graphs of karyotype of GC iPSCs. i. Representative action potential tracings recorded from father, proband, brother, mother and GC iPSC-CMs. Red arrows indicate arrhythmias. Dash lines indicate 0 mV. j–l. Bar graphs to compare arrhythmic incidence, SD of ISIs, and Vmax between different groups in i by One-way ANOVA (Tukey method). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 and ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001. m. Representative Na + current tracings isolated from father, proband, brother, mother and GC iPSC-CMs. n. Bar graph to compare the peak Na+ current density at −30 mV between different groups in m by One-way ANOVA (Tukey method). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 and ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001. o. Representative Ca2+ current tracings isolated from father, proband, brother, mother and GC iPSC-CMs. p. Bar graph to compare the peak Ca2+ current density at 0 mV between different groups in o by One-way ANOVA (Tukey method). n = 8–15. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 and ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001.