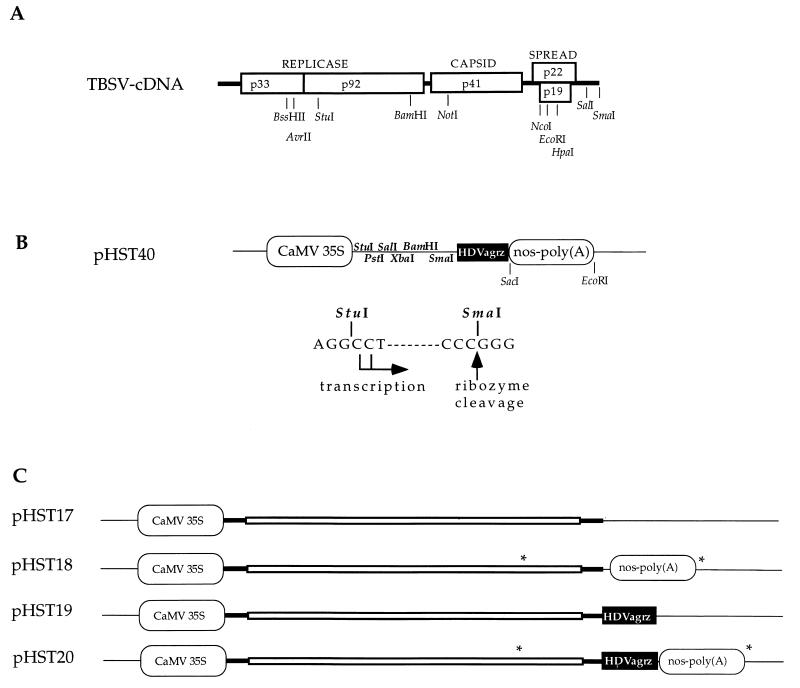
FIG. 1.
Plasmids and regulatory sequences. (A) Infectious cDNA of TBSV (12). The open reading frames are indicated by boxes, and encoded proteins (numbers show molecular masses, in kilodaltons) are provided with their function; thick lines represent untranslated sequences. Selected restriction enzyme sites that are relevant for this study are shown. (B) The cDNA cloning vector (pHST40) for in vivo transcription. Two alternative transcriptional start sites are indicated, and the HDVagrz RNA cleavage site is shown at the SmaI site on the DNA. Any cDNA can be cloned between the StuI and SmaI sites, which will facilitate in vivo transcription of RNAs with authentic 5′ and 3′ termini. Thin lines represent pUC18 sequences. (C) The plasmids pHST17 through pHST20 show the DNA-based TBSV constructs with the CaMV 35S promoter and the combinations of nos-poly(A) and/or HDVagrz at the 3′ end. The asterisks denote the positions of primers utilized to amplify the PCR products used in the assays described for Fig. 3.